“Chronic Disease Surveillance and Epidemiology – Part 8: Data Linkage in Chronic Disease Research
Related Articles Chronic Disease Surveillance and Epidemiology – Part 8: Data Linkage in Chronic Disease Research
- The Impact Of Chronic Disease On Family Dynamics
- Holistic Wellness Programs For Chronic Disease Patients – Part 5
- Integrative Care Models For Complex Chronic Diseases – Part 2: Implementation, Challenges, And Future Directions
- Disability Rights And Advocacy For Chronic Disease Patients – Part 3
- Chronic Disease Trends In Aging Populations – Part 7: The Role Of Technology And Innovation In Managing Geriatric Chronic Conditions
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Chronic Disease Surveillance and Epidemiology – Part 8: Data Linkage in Chronic Disease Research. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Chronic Disease Surveillance and Epidemiology – Part 8: Data Linkage in Chronic Disease Research
Chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases, are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. These conditions often develop over a long period and are influenced by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. Understanding the patterns, trends, and determinants of chronic diseases is essential for developing effective prevention and control strategies. Chronic disease surveillance and epidemiology play a crucial role in monitoring the burden of these diseases, identifying high-risk populations, and evaluating the impact of interventions.
As we delve deeper into the realm of chronic disease surveillance and epidemiology, one powerful tool that has gained significant traction in recent years is data linkage. Data linkage involves connecting records from different data sources that pertain to the same individual or entity. This technique enables researchers and public health professionals to create a more comprehensive picture of individuals’ health trajectories, risk factors, and outcomes. In this article, we will explore the concept of data linkage in chronic disease research, its benefits, challenges, and ethical considerations.
What is Data Linkage?
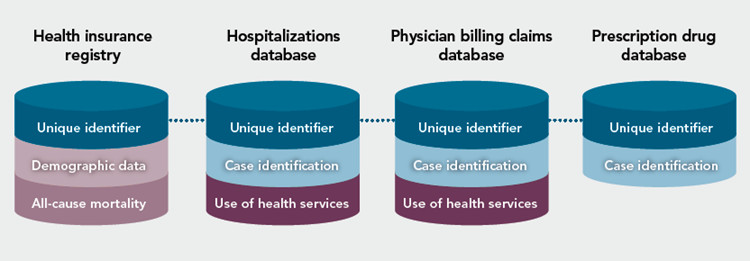
Data linkage, also known as record linkage or data matching, is the process of bringing together information from multiple data sources that relate to the same individual or entity. The goal is to create a more complete and informative dataset that can be used for research, surveillance, and public health purposes. Data linkage is typically performed using unique identifiers, such as social security numbers, medical record numbers, or other personal information. However, in cases where unique identifiers are not available or reliable, probabilistic matching techniques can be employed.
Benefits of Data Linkage in Chronic Disease Research
Data linkage offers numerous benefits in the context of chronic disease research:
- Enhanced Data Completeness: By linking data from different sources, researchers can fill in gaps in information and create a more comprehensive picture of individuals’ health histories, risk factors, and outcomes. For example, linking hospital discharge data with cancer registry data can provide insights into the incidence, treatment patterns, and survival rates of cancer patients.
- Improved Accuracy: Data linkage can help to improve the accuracy of information by cross-validating data from different sources. Discrepancies in data can be identified and resolved, leading to more reliable and valid research findings.
- Increased Statistical Power: By combining data from multiple sources, researchers can increase the sample size and statistical power of their studies. This is particularly important when studying rare diseases or outcomes.
- Longitudinal Studies: Data linkage enables researchers to conduct longitudinal studies that track individuals over time. This is essential for understanding the natural history of chronic diseases and identifying risk factors that contribute to their development.
- Evaluation of Interventions: Data linkage can be used to evaluate the impact of interventions aimed at preventing or controlling chronic diseases. By linking data on intervention exposure with data on health outcomes, researchers can assess the effectiveness of these interventions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Data linkage can be a cost-effective way to conduct research, as it leverages existing data sources rather than requiring the collection of new data.
Challenges of Data Linkage
Despite its many benefits, data linkage also presents several challenges:
- Data Quality: The quality of the data used for linkage can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of the results. Incomplete, inaccurate, or inconsistent data can lead to errors in the linkage process and biased findings.
- Data Security and Privacy: Data linkage involves the handling of sensitive personal information, which raises concerns about data security and privacy. It is essential to implement appropriate safeguards to protect the confidentiality of individuals’ data.
- Technical Complexity: Data linkage can be technically complex, requiring specialized expertise in data management, statistical analysis, and computer programming.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Data linkage must be conducted in accordance with all applicable laws and ethical guidelines. This includes obtaining informed consent from individuals whose data are being linked, as well as ensuring that the data are used for legitimate research purposes.
- Lack of Standardization: The lack of standardization in data collection and coding practices can make it difficult to link data from different sources.
Ethical Considerations in Data Linkage
Data linkage raises several ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed:
- Informed Consent: Obtaining informed consent from individuals whose data are being linked is essential to ensure that they are aware of the purpose of the linkage, the types of data being linked, and the potential risks and benefits of the linkage.
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting the security and privacy of individuals’ data is paramount. This includes implementing appropriate security measures to prevent unauthorized access to the data, as well as ensuring that the data are used only for legitimate research purposes.
- Transparency: Researchers should be transparent about the data linkage process, including the data sources being used, the linkage methods being employed, and the potential limitations of the data.
- Equity: Data linkage should be conducted in a way that promotes equity and avoids exacerbating existing health disparities. This includes ensuring that all populations are represented in the data and that the data are used to address the health needs of all communities.
- Beneficence: The potential benefits of data linkage should outweigh the potential risks. Researchers should strive to use data linkage to improve the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
Examples of Data Linkage in Chronic Disease Research
Data linkage has been used in a wide range of chronic disease research studies:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Data linkage has been used to study the risk factors for cardiovascular disease, the effectiveness of interventions to prevent heart attacks and strokes, and the long-term outcomes of patients with heart disease.
- Cancer: Data linkage has been used to study the incidence, prevalence, and survival rates of cancer patients, as well as to evaluate the effectiveness of cancer screening and treatment programs.
- Diabetes: Data linkage has been used to study the prevalence of diabetes, the risk factors for developing diabetes, and the effectiveness of interventions to prevent or manage diabetes.
- Chronic Respiratory Diseases: Data linkage has been used to study the prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases, the risk factors for developing these diseases, and the effectiveness of interventions to improve lung function and quality of life.
Conclusion
Data linkage is a powerful tool that can enhance chronic disease surveillance and epidemiology. By linking data from different sources, researchers can create a more comprehensive picture of individuals’ health trajectories, risk factors, and outcomes. Data linkage offers numerous benefits, including enhanced data completeness, improved accuracy, increased statistical power, and the ability to conduct longitudinal studies and evaluate interventions. However, data linkage also presents several challenges, including data quality, data security and privacy, technical complexity, and legal and ethical considerations. By carefully addressing these challenges and adhering to ethical guidelines, researchers can harness the power of data linkage to improve our understanding of chronic diseases and develop more effective prevention and control strategies.








Leave a Reply to The Most Common Mistakes In Heart Disease Management – fitlifedaily Cancel reply