“Understanding Chronic Diseases: Causes and Management – Part 7
Related Articles Understanding Chronic Diseases: Causes and Management – Part 7
- Educational Interventions For Chronic Disease Prevention: A Comprehensive Overview
- Mental Health Interventions For Chronic Disease Patients – Part 4
- Public Health Initiatives To Combat Chronic Illnesses – Part 2
- Cultural Perspectives On Chronic Disease Management – Part 5: Integrating Cultural Competence Into Healthcare Delivery
- Psychological Resilience In Chronic Disease Patients: Navigating Challenges And Fostering Well-being
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Understanding Chronic Diseases: Causes and Management – Part 7. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Chronic Diseases: Causes and Management – Part 7

Chronic diseases are long-lasting health conditions that cannot be cured but can be controlled. They are the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, accounting for a significant proportion of healthcare costs. Understanding the causes and management of chronic diseases is crucial for individuals, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to reduce their impact and improve quality of life.
The Burden of Chronic Diseases
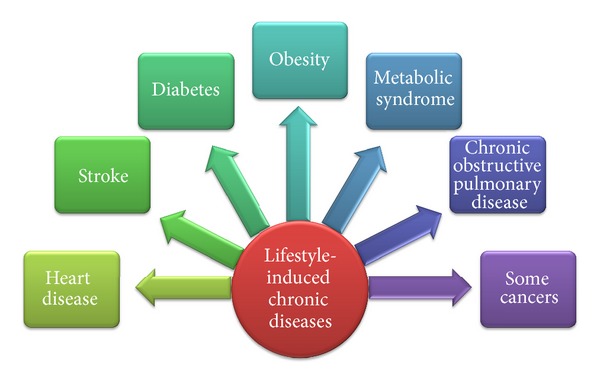
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and chronic lung diseases, are a growing global health concern. They are responsible for a significant percentage of deaths and disabilities worldwide, placing a heavy burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems.
Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases
Several risk factors contribute to the development of chronic diseases. These risk factors can be broadly categorized into modifiable and non-modifiable factors:
-
Modifiable Risk Factors:
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats increases the risk of obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain, muscle loss, and an increased risk of chronic diseases.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, cancer, and chronic lung diseases.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, heart problems, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
-
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:
- Age: The risk of developing chronic diseases increases with age.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can increase the risk of certain chronic diseases.
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of chronic diseases are at a higher risk of developing them.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups have a higher risk of developing specific chronic diseases.
Prevention Strategies for Chronic Diseases
Preventing chronic diseases is essential to reduce their impact on individuals and society. Several strategies can be implemented to prevent chronic diseases:
-
Promoting Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Healthy Diet: Encourage individuals to consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular Physical Activity: Promote regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, or swimming, for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Tobacco Cessation: Provide resources and support for individuals to quit smoking.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Educate individuals about the risks of excessive alcohol consumption and promote moderation.
-
Early Detection and Screening:
- Regular Check-ups: Encourage individuals to have regular check-ups with their healthcare provider to screen for risk factors and early signs of chronic diseases.
- Screening Programs: Implement screening programs for common chronic diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, to detect them early when they are more treatable.
-
Public Health Initiatives:
- Health Education Campaigns: Launch public health campaigns to raise awareness about chronic diseases and promote healthy lifestyle choices.
- Environmental Interventions: Implement policies to create environments that support healthy behaviors, such as access to healthy food options and safe places for physical activity.
- Taxation and Regulation: Implement taxes on unhealthy products, such as sugary drinks and tobacco, and regulate their availability to reduce consumption.
Management of Chronic Diseases
Managing chronic diseases involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication, and ongoing monitoring.
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: Individuals with chronic diseases may need to make dietary changes to manage their condition. For example, people with diabetes need to control their blood sugar levels through diet, while people with heart disease need to reduce their intake of saturated fats and cholesterol.
- Regular Exercise: Regular exercise is essential for managing many chronic diseases. It can help improve cardiovascular health, control weight, and reduce stress.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen many chronic diseases. Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress and improve overall health.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial for people with chronic lung diseases, heart disease, and cancer.
-
Medication:
- Prescription Medications: Many chronic diseases require medication to control symptoms and prevent complications. For example, people with diabetes may need insulin or oral medications to control their blood sugar levels, while people with heart disease may need medications to lower their blood pressure or cholesterol.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Some chronic diseases can be managed with over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers or antacids.
-
Ongoing Monitoring:
- Regular Check-ups: Individuals with chronic diseases need regular check-ups with their healthcare provider to monitor their condition and adjust their treatment plan as needed.
- Self-Monitoring: Many chronic diseases require self-monitoring, such as checking blood sugar levels for people with diabetes or monitoring blood pressure for people with hypertension.
Challenges in Managing Chronic Diseases
Managing chronic diseases can be challenging for individuals, healthcare professionals, and healthcare systems.
- Adherence to Treatment Plans: Many individuals with chronic diseases struggle to adhere to their treatment plans, which can lead to poor outcomes.
- Comorbidities: Individuals with chronic diseases often have multiple health conditions, which can complicate their management.
- Access to Care: Access to healthcare can be a barrier to managing chronic diseases, particularly for individuals in rural areas or with low incomes.
- Healthcare Costs: The cost of managing chronic diseases can be substantial, which can create financial barriers to care.
Strategies to Improve Chronic Disease Management
Several strategies can be implemented to improve chronic disease management:
-
Patient Education and Empowerment:
- Educate Patients: Provide patients with clear and concise information about their condition, treatment options, and self-management strategies.
- Empower Patients: Encourage patients to take an active role in their care by setting goals, making lifestyle changes, and monitoring their condition.
-
Care Coordination:
- Coordinate Care: Coordinate care among different healthcare providers to ensure that patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care.
- Care Management Programs: Implement care management programs to provide patients with individualized support and guidance.
-
Technology-Enabled Care:
- Telemedicine: Use telemedicine to provide remote monitoring and consultations to patients with chronic diseases.
- Mobile Health Apps: Develop mobile health apps to help patients track their symptoms, manage their medications, and communicate with their healthcare providers.
-
Policy and System-Level Changes:
- Improve Access to Care: Expand access to healthcare for individuals in underserved areas and with low incomes.
- Reduce Healthcare Costs: Implement policies to reduce the cost of managing chronic diseases, such as negotiating lower drug prices and promoting preventive care.
Conclusion
Chronic diseases are a significant public health challenge that requires a multifaceted approach to prevention and management. By addressing modifiable risk factors, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, implementing early detection and screening programs, and improving access to care, we can reduce the impact of chronic diseases and improve the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
Managing chronic diseases requires a collaborative effort between individuals, healthcare professionals, and policymakers. By working together, we can create a healthier future for all.







Leave a Reply