“Preventive Screening Guidelines for Chronic Conditions – Part 6
Related Articles Preventive Screening Guidelines for Chronic Conditions – Part 6
- The Impact Of Chronic Disease On Family Dynamics – Part 6
- Mental Health Interventions For Chronic Disease Patients – Part 5: Technological Approaches And The Future Of Integrated Care
- Workplace Accommodations For Employees With Chronic Diseases – Part 6
- Coping Strategies For Families Affected By Chronic Illness – Part 4: Fostering Resilience And Long-Term Well-being
- Chronic Disease Management In Low-Income Communities: Challenges, Strategies, And The Path Forward
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to Preventive Screening Guidelines for Chronic Conditions – Part 6. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Preventive Screening Guidelines for Chronic Conditions – Part 6
Chronic diseases are a significant public health challenge worldwide, contributing to a substantial portion of morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs. Early detection and management of these conditions through preventive screening can significantly improve health outcomes, reduce complications, and enhance the quality of life. This article, the sixth in a series, provides a comprehensive overview of preventive screening guidelines for various chronic conditions, aiming to equip healthcare professionals and individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about their health.
I. Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including heart disease and stroke, are the leading cause of death globally. Preventive screening plays a crucial role in identifying individuals at risk and implementing timely interventions to prevent or delay the onset of CVDs.
-
Blood Pressure Screening:
- Recommendation: Regular blood pressure screening is recommended for all adults aged 18 years and older.
- Frequency: At least once every two years for individuals with normal blood pressure (less than 120/80 mmHg) and more frequently for those with elevated blood pressure or risk factors for hypertension.
- Rationale: Hypertension is a major risk factor for CVDs, and early detection and management can significantly reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
-
Cholesterol Screening:
- Recommendation: Lipid panel screening, including total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglycerides, is recommended for adults starting at age 20.
- Frequency: Every 4-6 years for individuals with normal cholesterol levels and more frequently for those with elevated cholesterol or risk factors for CVDs.
- Rationale: High LDL-C and low HDL-C are major risk factors for atherosclerosis, a condition that can lead to heart disease and stroke.
-
Diabetes Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for type 2 diabetes is recommended for adults aged 35 to 70 years who are overweight or obese (BMI ≥25 kg/m2) or have other risk factors for diabetes.
- Frequency: Every 3 years for individuals with normal blood sugar levels and more frequently for those with prediabetes or risk factors for diabetes.
- Rationale: Diabetes is a major risk factor for CVDs, and early detection and management can significantly reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG):
- Recommendation: Routine ECG screening is not recommended for asymptomatic adults without risk factors for CVDs.
- Rationale: ECG screening may lead to false-positive results, unnecessary testing, and anxiety. However, ECG may be considered for individuals with specific risk factors or symptoms suggestive of heart disease.
-
Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) Score:
- Recommendation: CAC scoring may be considered for individuals at intermediate risk for CVDs to help refine risk stratification and guide treatment decisions.
- Rationale: CAC scoring can help identify individuals with subclinical atherosclerosis who may benefit from more aggressive risk factor modification.
II. Cancer
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, and early detection through preventive screening can significantly improve survival rates and quality of life.
-
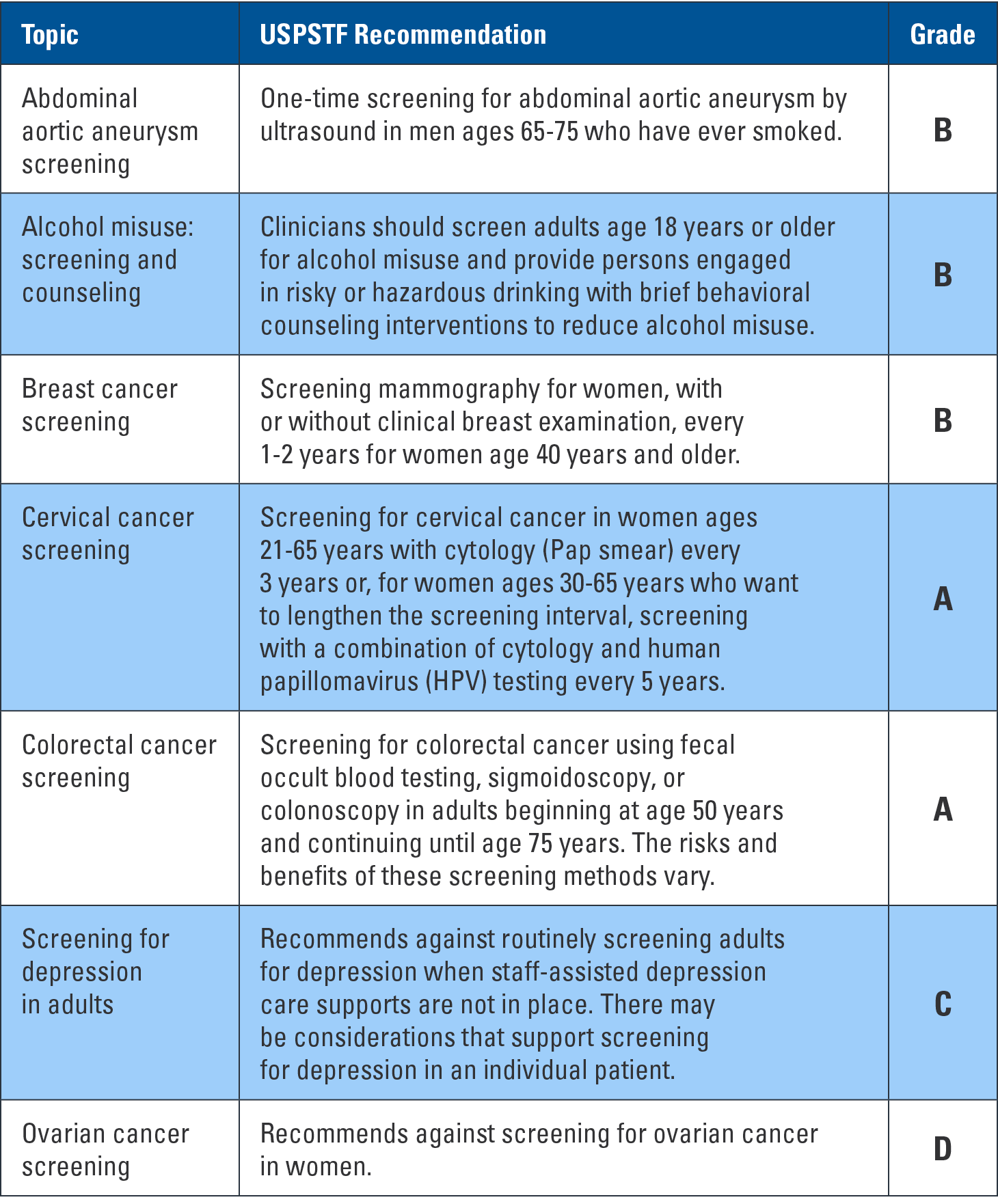
Breast Cancer Screening:
- Recommendation: Mammography is recommended for women aged 50 to 74 years.
- Frequency: Every two years.
- Rationale: Mammography can detect breast cancer at an early stage when it is more treatable.
- Additional Considerations: Women aged 40 to 49 years should discuss the risks and benefits of mammography with their healthcare provider.
-
Cervical Cancer Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for cervical cancer is recommended for women aged 21 to 65 years.
- Frequency:
- Pap test: Every three years for women aged 21 to 29 years.
- Pap test and HPV test (co-testing): Every five years for women aged 30 to 65 years.
- Rationale: Cervical cancer screening can detect precancerous lesions and early-stage cancer, allowing for timely treatment.
-
Colorectal Cancer Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for colorectal cancer is recommended for adults aged 45 to 75 years.
- Screening Options:
- Fecal occult blood test (FOBT): Annually.
- Fecal immunochemical test (FIT): Annually.
- Stool DNA test: Every one to three years.
- Colonoscopy: Every 10 years.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy: Every 5 years.
- CT colonography: Every 5 years.
- Rationale: Colorectal cancer screening can detect precancerous polyps and early-stage cancer, allowing for timely treatment.
-
Lung Cancer Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) is recommended for adults aged 50 to 80 years who have a 20 pack-year smoking history and are currently smoking or have quit within the past 15 years.
- Frequency: Annually.
- Rationale: Lung cancer screening can detect lung cancer at an early stage when it is more treatable.
-
Prostate Cancer Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for prostate cancer with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing is not routinely recommended for all men.
- Rationale: PSA testing may lead to false-positive results, unnecessary biopsies, and overtreatment.
- Additional Considerations: Men aged 55 to 69 years should discuss the risks and benefits of PSA testing with their healthcare provider.
III. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by decreased bone density, increasing the risk of fractures. Preventive screening can help identify individuals at risk and implement interventions to prevent fractures.
-
Bone Density Screening:
- Recommendation: Bone density screening with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) is recommended for women aged 65 years and older and for younger women with risk factors for osteoporosis.
- Frequency: Every two years for individuals with osteoporosis or risk factors for osteoporosis.
- Rationale: Bone density screening can identify individuals with osteoporosis or osteopenia, allowing for timely treatment to prevent fractures.
IV. Mental Health Conditions
Mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, are common and can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Preventive screening can help identify individuals at risk and provide timely interventions.
-
Depression Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for depression is recommended for all adults.
- Frequency: Annually.
- Rationale: Depression is a common condition that can be effectively treated with medication and therapy.
-
Anxiety Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for anxiety is recommended for adults with risk factors for anxiety.
- Frequency: As needed.
- Rationale: Anxiety is a common condition that can be effectively treated with medication and therapy.
V. Infectious Diseases
Preventive screening for infectious diseases can help identify individuals who are infected and prevent the spread of disease.
-
HIV Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for HIV is recommended for all adults aged 13 to 64 years.
- Frequency: At least once in a lifetime and more frequently for individuals with risk factors for HIV.
- Rationale: HIV screening can identify individuals who are infected and allow for timely treatment to prevent the progression of the disease.
-
Hepatitis C Screening:
- Recommendation: Screening for hepatitis C is recommended for all adults aged 18 to 79 years.
- Frequency: At least once in a lifetime and more frequently for individuals with risk factors for hepatitis C.
- Rationale: Hepatitis C screening can identify individuals who are infected and allow for timely treatment to prevent the progression of the disease.
VI. Conclusion
Preventive screening guidelines for chronic conditions are essential for early detection, management, and prevention of disease. Healthcare professionals should be knowledgeable about these guidelines and work with individuals to develop personalized screening plans based on their age, sex, risk factors, and preferences. By implementing preventive screening strategies, we can improve health outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance the quality of life for individuals and communities.
It is important to note that these guidelines are based on current evidence and may be subject to change as new research becomes available. Healthcare professionals should stay up-to-date on the latest recommendations and use their clinical judgment to make informed decisions about preventive screening.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.







Leave a Reply