“Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 6
Related Articles Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 6
- The Impact Of Chronic Illness On Mental Health – Part 6
- Long-Term Effects Of Chronic Illness On Children
- Public Health Initiatives To Combat Chronic Illnesses – Part 4: Leveraging Technology And Data Analytics
- Patient Education And Health Literacy In Chronic Disease Care – Part 3
- The Role Of Genetics In Chronic Disease Development – Part 5: The Future Of Genetic Research And Personalized Medicine
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 6. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 6
Introduction
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and arthritis, are the leading causes of death and disability in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), six in ten adults in the United States have a chronic disease. Additionally, four in ten adults have two or more chronic diseases. Chronic diseases are also a major driver of health care costs in the United States.
Living with a chronic disease can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health. People with chronic diseases are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. In fact, studies have shown that people with chronic diseases are two to three times more likely to develop depression than people without chronic diseases.
The relationship between chronic disease and mental health is complex. Chronic diseases can cause mental health problems, and mental health problems can make chronic diseases worse. For example, chronic pain can lead to depression, and depression can make chronic pain worse. Similarly, stress can worsen chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
The good news is that there are effective mental health interventions that can help people with chronic diseases manage their mental health and improve their overall health. This article will discuss some of the most common and effective mental health interventions for people with chronic diseases.
Types of Mental Health Interventions
There are a variety of mental health interventions that can be helpful for people with chronic diseases. Some of the most common interventions include:
-
Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, involves working with a therapist to identify and change negative thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Psychotherapy can be helpful for people with chronic diseases who are experiencing depression, anxiety, or other mental health conditions.
-
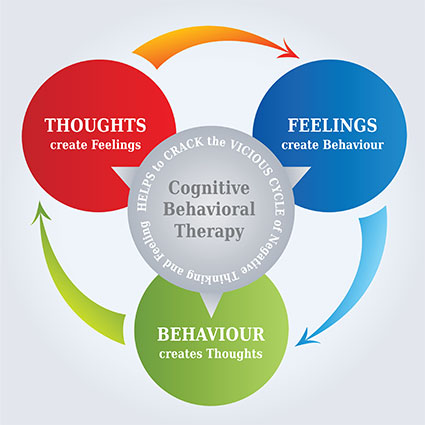
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors. CBT can be helpful for people with chronic diseases who are experiencing pain, fatigue, or other symptoms.
-
Mindfulness-Based Interventions: Mindfulness-based interventions involve training people to pay attention to the present moment without judgment. Mindfulness-based interventions can be helpful for people with chronic diseases who are experiencing stress, anxiety, or pain.
-
Exercise: Exercise has been shown to improve mental health in people with chronic diseases. Exercise can help to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. It can also help to improve sleep and energy levels.
-
Support Groups: Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for people with chronic diseases to share their experiences and learn from others. Support groups can help people to feel less alone and more connected.
-
Medication: Medication can be helpful for people with chronic diseases who are experiencing depression, anxiety, or other mental health conditions. Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can help to improve mood, reduce anxiety, and improve sleep.
Effectiveness of Mental Health Interventions
A growing body of evidence supports the effectiveness of mental health interventions for people with chronic diseases. Studies have shown that mental health interventions can help to:
- Reduce depression and anxiety symptoms
- Improve mood and quality of life
- Reduce pain and fatigue
- Improve sleep
- Increase adherence to medical treatment
- Reduce hospitalizations
- Improve overall health outcomes
Specific Mental Health Interventions for Specific Chronic Diseases
While the interventions listed above are generally effective for people with chronic diseases, some interventions may be particularly helpful for specific conditions.
-
Heart Disease: People with heart disease are at increased risk for depression and anxiety. Mental health interventions that can be helpful for people with heart disease include CBT, mindfulness-based interventions, and exercise.
-
Diabetes: People with diabetes are also at increased risk for depression and anxiety. Mental health interventions that can be helpful for people with diabetes include CBT, mindfulness-based interventions, and support groups.
-
Cancer: Cancer can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health. Mental health interventions that can be helpful for people with cancer include psychotherapy, CBT, mindfulness-based interventions, and support groups.
-
Chronic Pain: Chronic pain can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. Mental health interventions that can be helpful for people with chronic pain include CBT, mindfulness-based interventions, and exercise.
Challenges to Accessing Mental Health Care
Despite the effectiveness of mental health interventions, many people with chronic diseases do not have access to the care they need. Some of the challenges to accessing mental health care include:
- Stigma: There is still a stigma associated with mental illness, which can prevent people from seeking help.
- Cost: Mental health care can be expensive, and many people do not have insurance coverage for mental health services.
- Lack of providers: There is a shortage of mental health providers, particularly in rural areas.
- Transportation: People with chronic diseases may have difficulty getting to mental health appointments.
- Lack of awareness: Many people with chronic diseases are not aware of the mental health resources that are available to them.
Strategies to Improve Access to Mental Health Care
There are a number of strategies that can be used to improve access to mental health care for people with chronic diseases. These strategies include:
- Reducing stigma: Public education campaigns can help to reduce the stigma associated with mental illness.
- Increasing insurance coverage: Expanding insurance coverage for mental health services can make care more affordable.
- Training more providers: Increasing the number of mental health providers can help to meet the demand for services.
- Using technology: Telehealth can be used to provide mental health services to people in rural areas or who have difficulty getting to appointments.
- Integrating mental health care into primary care: Integrating mental health care into primary care settings can make it easier for people to access care.
The Role of Integrated Care
Integrated care is a model of care that brings together physical and mental health services in a coordinated way. Integrated care can be particularly helpful for people with chronic diseases, as it can help to address both their physical and mental health needs.
There are a number of different models of integrated care. Some common models include:
- Co-location: Co-location involves locating mental health providers in the same physical space as primary care providers.
- Collaboration: Collaboration involves primary care providers and mental health providers working together to coordinate care.
- Integration: Integration involves fully integrating mental health care into primary care settings.
The Future of Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients
The future of mental health interventions for chronic disease patients is bright. As our understanding of the relationship between chronic disease and mental health grows, we are developing more effective and targeted interventions. We are also finding new ways to deliver mental health care, such as through telehealth and integrated care models.
Some of the emerging trends in mental health interventions for chronic disease patients include:
- Personalized medicine: Personalized medicine involves tailoring treatment to the individual patient. This approach can be particularly helpful for people with chronic diseases, as it can take into account their individual needs and preferences.
- Digital health: Digital health technologies, such as mobile apps and wearable devices, are being used to deliver mental health interventions. These technologies can make care more accessible and convenient.
- Prevention: Prevention efforts are focused on preventing mental health problems in people with chronic diseases. These efforts may include education, screening, and early intervention.
Conclusion
Living with a chronic disease can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health. However, there are effective mental health interventions that can help people with chronic diseases manage their mental health and improve their overall health. By addressing the challenges to accessing mental health care and by embracing new models of care, we can ensure that all people with chronic diseases have access to the mental health care they need.
It is important for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals living with chronic diseases to work together to promote mental health and well-being. This includes raising awareness about the importance of mental health, reducing stigma, increasing access to care, and developing innovative interventions. By working together, we can improve the lives of people living with chronic diseases.








Leave a Reply