“Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 4
Related Articles Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 4
- Environmental Factors And Chronic Disease Risk
- Palliative Care And Quality Of Life For Chronic Illness Patients – Part 4
- Workplace Accommodations For Employees With Chronic Diseases – Part 4
- Holistic Wellness Programs For Chronic Disease Patients
- The Impact Of Chronic Illness On Mental Health
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 4. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Mental Health Interventions for Chronic Disease Patients – Part 4
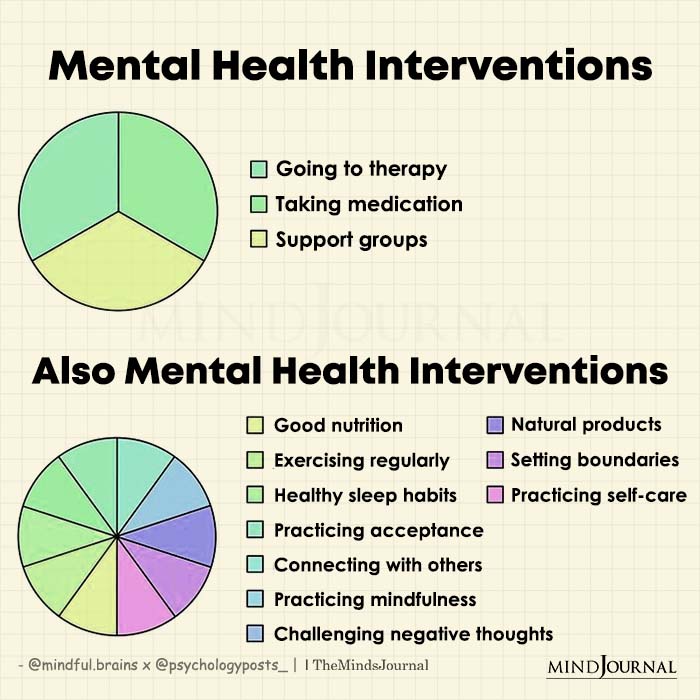
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and respiratory illnesses, are the leading cause of death and disability worldwide. They significantly impact individuals’ physical health and profoundly affect their mental well-being. The emotional burden of managing a chronic illness can lead to various mental health challenges, including depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders. Therefore, integrating mental health interventions into chronic disease management is essential for holistic patient care.
This article, the fourth in a series, explores further mental health interventions tailored to the unique needs of individuals living with chronic diseases. It examines various therapeutic approaches, lifestyle modifications, and support systems that can significantly improve mental well-being and overall quality of life for these patients.
1. Mindfulness-Based Interventions (MBIs)
Mindfulness-Based Interventions (MBIs) are increasingly recognized as valuable tools for managing the mental health challenges associated with chronic diseases. MBIs involve cultivating present moment awareness without judgment, allowing individuals to observe their thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations without getting carried away by them.
How MBIs Work:
MBIs typically involve a combination of meditation practices, body scans, and mindful movement exercises. These practices help individuals develop a greater awareness of their internal experiences, allowing them to respond to stressors and negative emotions more effectively. By focusing on the present moment, individuals can reduce rumination on past events or worries about the future, which are common contributors to anxiety and depression in chronic disease patients.
Benefits of MBIs for Chronic Disease Patients:
- Stress Reduction: MBIs have been shown to reduce stress hormone levels and promote relaxation, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals coping with the demands of managing a chronic illness.
- Improved Mood: Regular mindfulness practice can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, leading to a more positive outlook on life.
- Pain Management: MBIs can help individuals develop a greater acceptance of chronic pain and learn to manage it more effectively.
- Enhanced Self-Awareness: MBIs promote self-awareness, allowing individuals to identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors that may be contributing to their distress.
Examples of MBIs:
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): This structured program typically involves eight weekly sessions and teaches participants various mindfulness techniques, including meditation, body scan, and yoga.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): This therapy combines mindfulness practices with cognitive behavioral techniques to help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to depression and anxiety.
2. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of psychotherapy that helps individuals accept difficult thoughts and feelings rather than struggling against them. ACT emphasizes the importance of identifying personal values and taking action towards living a meaningful life, even in the face of chronic illness.
How ACT Works:
ACT is based on the idea that attempts to control or suppress negative thoughts and feelings can be counterproductive and lead to increased distress. Instead, ACT encourages individuals to accept these experiences as a natural part of life and focus on taking action towards their values. ACT uses various techniques, including mindfulness, cognitive defusion, and values clarification, to help individuals develop psychological flexibility and live more fulfilling lives.
Benefits of ACT for Chronic Disease Patients:
- Increased Psychological Flexibility: ACT helps individuals become more flexible in their thinking and behavior, allowing them to respond to challenges more effectively.
- Improved Quality of Life: By focusing on values and taking action towards meaningful goals, ACT can help individuals experience a greater sense of purpose and fulfillment in life.
- Reduced Emotional Distress: ACT can help individuals reduce the impact of negative thoughts and feelings on their daily lives, leading to improved mood and overall well-being.
- Enhanced Coping Skills: ACT provides individuals with practical tools and strategies for managing the emotional challenges of living with a chronic illness.
3. Peer Support Groups
Peer support groups provide a safe and supportive environment where individuals with chronic diseases can connect with others who understand their experiences. These groups offer opportunities for sharing information, emotional support, and practical advice.
How Peer Support Groups Work:
Peer support groups can be facilitated by healthcare professionals or led by individuals with lived experience of chronic illness. Groups typically meet regularly, either in person or online, and provide a space for members to share their stories, ask questions, and offer support to one another. Peer support groups can focus on specific chronic diseases or address broader themes related to living with chronic illness, such as coping with pain, managing stress, or navigating the healthcare system.
Benefits of Peer Support Groups for Chronic Disease Patients:
- Reduced Isolation: Peer support groups can help individuals feel less alone in their experiences and provide a sense of community.
- Emotional Support: Group members can offer empathy, understanding, and encouragement to one another, which can be particularly valuable during difficult times.
- Information Sharing: Peer support groups can be a valuable source of information about chronic diseases, treatment options, and coping strategies.
- Improved Coping Skills: By sharing their experiences and learning from others, individuals can develop new coping skills and strategies for managing their chronic illness.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing chronic diseases and promoting mental well-being. These modifications involve making changes to daily habits and routines to improve physical and mental health.
Examples of Lifestyle Modifications:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity has numerous benefits for both physical and mental health. Exercise can help reduce stress, improve mood, and boost self-esteem.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients for optimal physical and mental functioning.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for physical and mental health. Sleep deprivation can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Social Connection: Maintaining strong social connections is crucial for mental health. Spending time with loved ones, participating in social activities, and volunteering can help reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation.
5. Collaborative Care Models
Collaborative care models integrate mental health services into primary care settings, making it easier for individuals with chronic diseases to access the mental health support they need.
How Collaborative Care Models Work:
Collaborative care models typically involve a team of healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, mental health specialists, and care managers, who work together to provide comprehensive care to patients. Mental health specialists may provide consultation to primary care physicians, offer brief therapy interventions, or refer patients to specialized mental health services. Care managers play a vital role in coordinating care, providing education and support to patients, and monitoring their progress.
Benefits of Collaborative Care Models for Chronic Disease Patients:
- Improved Access to Mental Health Services: Collaborative care models make it easier for individuals to access mental health services, particularly in underserved areas where mental health specialists may be scarce.
- Integrated Care: Collaborative care models ensure that mental health and physical health are addressed in a coordinated manner, leading to more holistic and effective care.
- Reduced Stigma: Integrating mental health services into primary care settings can help reduce the stigma associated with mental illness, making it more acceptable for individuals to seek help.
- Improved Outcomes: Studies have shown that collaborative care models can lead to improved mental health outcomes, better chronic disease management, and increased patient satisfaction.
6. Technology-Based Interventions
Technology-based interventions, such as mobile apps, online support groups, and telehealth services, offer convenient and accessible ways for individuals with chronic diseases to manage their mental health.
Examples of Technology-Based Interventions:
- Mobile Apps: Many mobile apps offer guided meditations, stress management techniques, and mood tracking tools. These apps can be used to promote mindfulness, reduce stress, and monitor mental health symptoms.
- Online Support Groups: Online support groups provide a virtual space for individuals with chronic diseases to connect with others, share their experiences, and offer support to one another.
- Telehealth Services: Telehealth services allow individuals to receive mental health care remotely, through video conferencing or phone calls. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who live in rural areas or have difficulty traveling to see a mental health professional.
Conclusion
Integrating mental health interventions into chronic disease management is essential for providing holistic care to patients. Mindfulness-based interventions, acceptance and commitment therapy, peer support groups, lifestyle modifications, collaborative care models, and technology-based interventions are all valuable tools for improving the mental well-being and overall quality of life for individuals living with chronic diseases. By addressing the emotional challenges associated with chronic illness, healthcare professionals can help patients live more fulfilling and meaningful lives.







Leave a Reply