“Long-Term Effects of Chronic Illness on Children
Related Articles Long-Term Effects of Chronic Illness on Children
- Lifestyle Changes To Manage Chronic Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide
- Holistic Approaches To Chronic Disease Prevention
- Emerging Therapies For Managing Chronic Conditions: A Glimpse Into The Future Of Healthcare
- Psychological Resilience In Chronic Disease Patients: Navigating Challenges And Fostering Well-being
- Lifestyle Changes To Manage Chronic Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Long-Term Effects of Chronic Illness on Children. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Long-Term Effects of Chronic Illness on Children
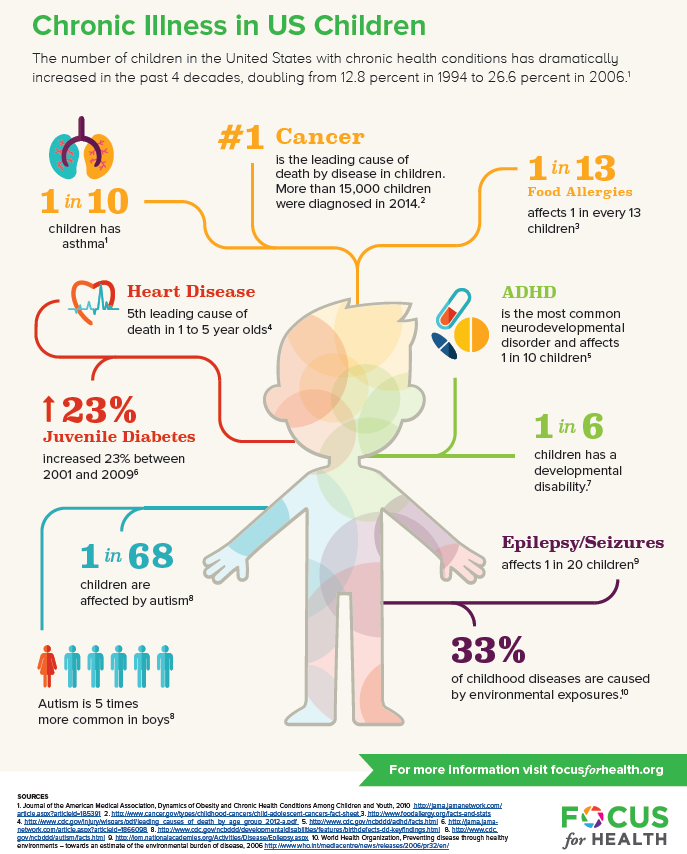
Chronic illnesses, defined as health conditions that last for more than a year and require ongoing medical attention or limit activities of daily living, are increasingly prevalent among children. These conditions, ranging from asthma and diabetes to cancer and congenital disorders, not only impact a child’s physical health but also significantly affect their emotional, social, and cognitive development. Understanding the long-term effects of chronic illness on children is crucial for providing comprehensive care and support to help them lead fulfilling lives.
Physical Health Impacts
The most immediate and obvious effects of chronic illness on children are physical. Depending on the specific condition, children may experience:
- Pain and Discomfort: Chronic pain is a common symptom in many illnesses, such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and sickle cell anemia. Persistent pain can lead to fatigue, sleep disturbances, and reduced mobility, significantly impacting a child’s quality of life.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome, cancer, and heart disease can cause debilitating fatigue, making it difficult for children to participate in everyday activities, attend school, and engage in social interactions.
- Growth and Development Delays: Certain illnesses, such as cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, and growth hormone deficiencies, can interfere with normal growth and development. Malnutrition, medication side effects, and the disease process itself can all contribute to these delays.
- Physical Limitations: Chronic conditions can limit a child’s physical abilities, making it challenging to participate in sports, play with peers, and perform daily tasks. This can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and low self-esteem.
- Increased Susceptibility to Infections: Some chronic illnesses, particularly those affecting the immune system, can increase a child’s risk of infections. Frequent infections can lead to hospitalizations, missed school days, and further complications.
Emotional and Psychological Impacts
Living with a chronic illness can take a significant toll on a child’s emotional and psychological well-being. Common emotional challenges include:
- Anxiety and Depression: The uncertainty, pain, and limitations associated with chronic illness can trigger anxiety and depression in children. They may worry about their health, future, and ability to live a normal life.
- Low Self-Esteem and Body Image Issues: Chronic illnesses can alter a child’s appearance, physical abilities, and social interactions, leading to feelings of inadequacy, shame, and low self-esteem.
- Grief and Loss: Children with chronic illnesses may experience grief over the loss of their previous health, abilities, and sense of normalcy. They may also grieve the loss of future opportunities and dreams.
- Anger and Frustration: Dealing with chronic symptoms, medical treatments, and limitations can lead to anger, frustration, and resentment. Children may lash out at family members, healthcare providers, or themselves.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Traumatic medical experiences, such as invasive procedures, hospitalizations, and life-threatening events, can lead to PTSD in children. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance behaviors, and hyperarousal.
Social Impacts
Chronic illness can significantly impact a child’s social life and relationships:
- Social Isolation: Children with chronic illnesses may experience social isolation due to frequent absences from school, limitations in physical activities, and feelings of being different from their peers.
- Difficulty Forming and Maintaining Friendships: Chronic illness can make it challenging for children to form and maintain friendships. They may feel self-conscious about their condition, worry about being a burden to others, or have difficulty participating in social activities.
- Bullying and Stigma: Children with chronic illnesses may be targets of bullying and stigma. They may be teased, excluded, or discriminated against because of their condition.
- Strain on Family Relationships: Chronic illness can place a significant strain on family relationships. Parents may experience stress, financial difficulties, and emotional exhaustion. Siblings may feel neglected or resentful of the attention given to the child with the illness.
- Impact on School Performance: Frequent absences, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties can negatively impact a child’s school performance. They may struggle to keep up with their peers, experience learning difficulties, and have difficulty concentrating.
Cognitive Impacts
Chronic illness can also affect a child’s cognitive abilities:
- Attention and Concentration Problems: Chronic pain, fatigue, and medication side effects can impair attention and concentration, making it difficult for children to focus in school and complete tasks.
- Memory Difficulties: Some chronic illnesses, such as epilepsy and autoimmune disorders, can affect memory and cognitive function. Children may have difficulty remembering information, learning new skills, and solving problems.
- Executive Function Deficits: Executive functions, such as planning, organization, and self-regulation, can be impaired in children with chronic illnesses. This can lead to difficulties with academic performance, social interactions, and daily living skills.
- Processing Speed Slowdown: Chronic illness can slow down a child’s processing speed, making it difficult for them to quickly understand and respond to information.
- Learning Disabilities: Children with chronic illnesses are at a higher risk of developing learning disabilities. These disabilities can affect reading, writing, math, and other academic skills.
Long-Term Outcomes
The long-term outcomes for children with chronic illnesses vary depending on the specific condition, its severity, and the availability of appropriate medical and psychosocial support. However, some common long-term challenges include:
- Increased Risk of Mental Health Problems: Children with chronic illnesses are at a higher risk of developing mental health problems in adulthood, such as anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
- Difficulty with Social Adjustment: Chronic illness can make it difficult for children to form and maintain relationships, find employment, and live independently in adulthood.
- Lower Educational Attainment: Children with chronic illnesses may have lower educational attainment than their peers due to frequent absences, learning difficulties, and cognitive impairments.
- Increased Healthcare Costs: Chronic illness can lead to increased healthcare costs throughout a person’s lifetime.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Chronic illness can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life, affecting their physical, emotional, social, and cognitive well-being.
Interventions and Support
Early intervention and comprehensive support are crucial for mitigating the long-term effects of chronic illness on children. Effective interventions include:
- Medical Management: Proper medical management is essential for controlling symptoms, preventing complications, and improving a child’s overall health.
- Psychological Support: Psychotherapy, counseling, and support groups can help children cope with the emotional challenges of chronic illness, improve their self-esteem, and develop coping skills.
- Educational Support: Individualized education plans (IEPs) and accommodations can help children with chronic illnesses succeed in school.
- Social Support: Encouraging social interaction, participation in extracurricular activities, and peer support groups can help children combat social isolation and build friendships.
- Family Support: Providing support and education to families can help them cope with the challenges of raising a child with a chronic illness.
- Advocacy: Advocating for the rights and needs of children with chronic illnesses can help ensure that they receive the resources and support they need to thrive.
Conclusion
Chronic illnesses can have profound and long-lasting effects on children’s physical, emotional, social, and cognitive development. By understanding these effects and providing comprehensive medical, psychological, educational, and social support, we can help children with chronic illnesses lead fulfilling lives and reach their full potential. Early intervention, ongoing management, and a supportive environment are essential for mitigating the long-term impact of chronic illness and promoting the well-being of these vulnerable children.







Leave a Reply