“Heart Rate Zones and Cardio Fitness: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles Heart Rate Zones and Cardio Fitness: A Comprehensive Guide
- Financial Challenges Of Living With Chronic Illness – Part 7: Navigating The Labyrinth Of Government Assistance Programs
- The Impact Of Chronic Disease On Family Dynamics – Part 5: Navigating Long-Term Care, Inheritance, And End-of-Life Decisions
- Understanding Chronic Diseases: Causes And Management – Part 5
- Supportive Care In Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
- The Role Of Stress In Chronic Disease Progression – Part 5: Integrative Approaches To Stress Management For Chronic Disease Patients
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Heart Rate Zones and Cardio Fitness: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Heart Rate Zones and Cardio Fitness: A Comprehensive Guide

Cardiovascular fitness, often referred to as cardio fitness, is a vital component of overall health and well-being. It reflects the efficiency of your heart, lungs, and blood vessels in delivering oxygen to working muscles during sustained physical activity. Achieving and maintaining good cardio fitness offers numerous benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved energy levels, and enhanced quality of life.
Understanding heart rate zones is crucial for optimizing your cardio workouts and achieving your fitness goals. Heart rate zones are specific ranges of heartbeats per minute (BPM) that correspond to different levels of exercise intensity. By monitoring your heart rate and training within specific zones, you can tailor your workouts to improve different aspects of your cardio fitness.
Understanding Heart Rate
Heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute. It’s a reliable indicator of how hard your body is working during physical activity. Your heart rate increases as your body demands more oxygen to fuel your muscles.
- Resting Heart Rate (RHR): Your heart rate when you’re at rest, typically measured in the morning after waking up. A lower RHR generally indicates better cardio fitness.
- Maximum Heart Rate (MHR): The highest number of times your heart can beat per minute during maximal exertion. It’s often estimated using formulas, but an exercise stress test provides the most accurate measurement.
- Heart Rate Reserve (HRR): The difference between your MHR and RHR. It represents the range of heart rates available to you during exercise.
Calculating Your Maximum Heart Rate
The most common formula for estimating maximum heart rate (MHR) is:
- MHR = 220 – Age
However, this formula has limitations and may not be accurate for everyone, especially for individuals with very high or low fitness levels. More accurate formulas include:
- MHR = 208 – (0.7 x Age) (Tanaka formula)
- MHR = 206.9 – (0.67 x Age) (Gellish formula)
For the most precise assessment, a supervised exercise stress test conducted by a healthcare professional is recommended.
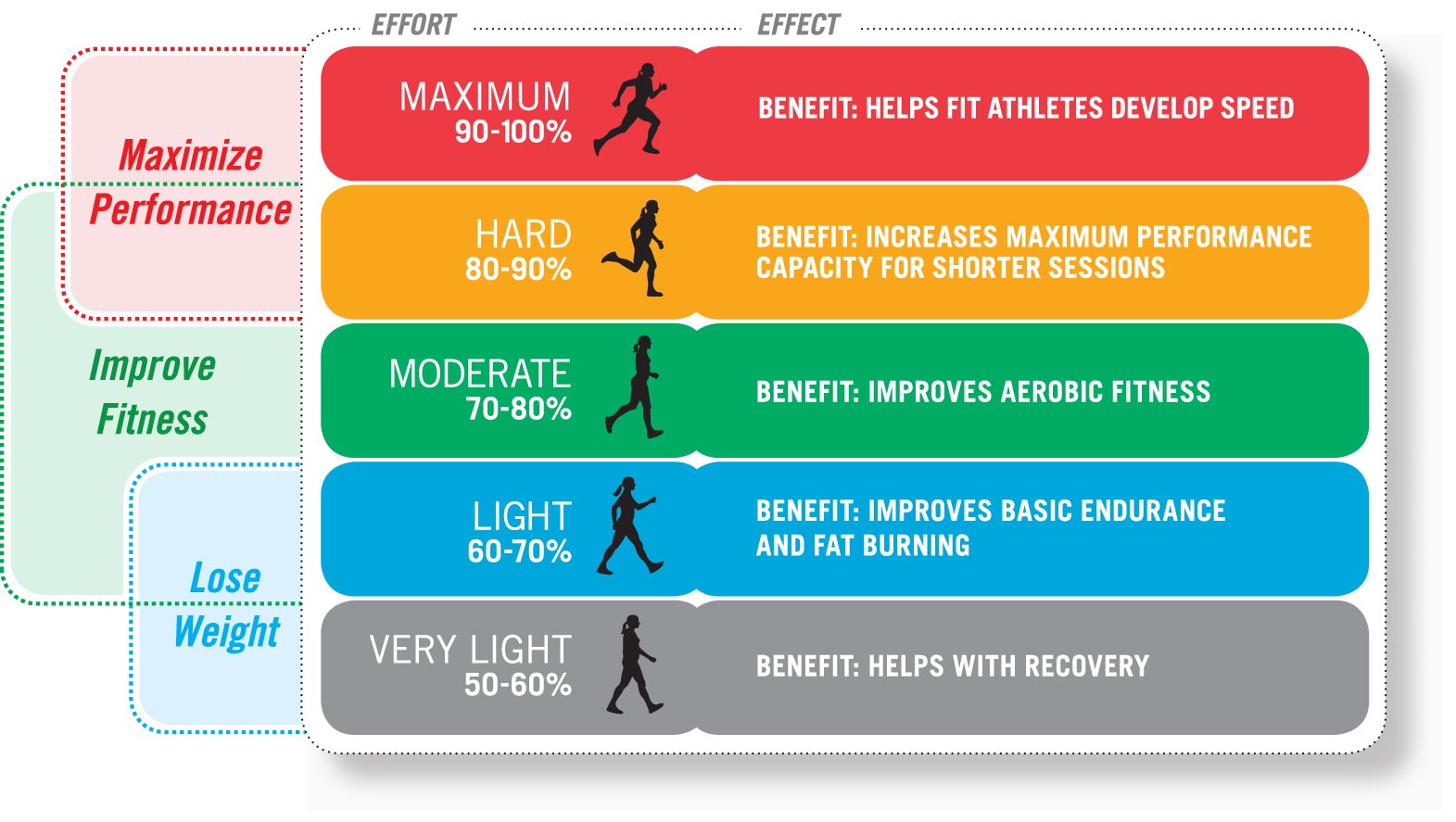
Heart Rate Zones Explained
Heart rate zones are typically expressed as percentages of your maximum heart rate (MHR) or heart rate reserve (HRR). Each zone corresponds to a specific intensity level and offers distinct benefits. The five primary heart rate zones are:
-
Zone 1: Very Light Intensity (50-60% of MHR)
- Description: This zone involves very light activity, such as a leisurely walk or stretching.
- Benefits: Improves recovery, reduces stress, and can be sustained for long periods.
- Suitable For: Warm-ups, cool-downs, active recovery days, and beginners.
-
Zone 2: Light Intensity (60-70% of MHR)
- Description: This zone involves light to moderate activity, such as a brisk walk or light jogging.
- Benefits: Improves basic endurance and fat burning, enhances cardiovascular health.
- Suitable For: Long-duration workouts, building a base level of fitness, and fat-burning workouts.
-
Zone 3: Moderate Intensity (70-80% of MHR)
- Description: This zone involves moderate to vigorous activity, such as jogging or cycling at a steady pace.
- Benefits: Improves cardiovascular fitness, increases aerobic capacity, and builds muscle endurance.
- Suitable For: Interval training, tempo runs, and building overall fitness.
-
Zone 4: Hard Intensity (80-90% of MHR)
- Description: This zone involves vigorous activity, such as running at a fast pace or intense cycling.
- Benefits: Improves speed, power, and anaerobic capacity, and increases lactate threshold.
- Suitable For: High-intensity interval training (HIIT), speed work, and advanced training.
-
Zone 5: Maximum Intensity (90-100% of MHR)
- Description: This zone involves maximal exertion, such as sprinting or all-out efforts.
- Benefits: Improves speed, power, and anaerobic capacity, and increases tolerance to high-intensity exercise.
- Suitable For: Short bursts of maximum effort, advanced training, and competitive events.
Benefits of Training in Different Heart Rate Zones
- Zone 1: Promotes recovery and stress reduction. It’s ideal for active recovery days and warm-ups.
- Zone 2: Enhances fat burning and builds a foundation of cardiovascular fitness. It’s suitable for long-duration workouts and improving endurance.
- Zone 3: Improves cardiovascular fitness and increases aerobic capacity. It’s effective for building overall fitness and enhancing endurance.
- Zone 4: Increases speed, power, and anaerobic capacity. It’s ideal for HIIT workouts and improving performance in high-intensity activities.
- Zone 5: Maximizes speed, power, and anaerobic capacity. It’s suitable for short bursts of maximal effort and advanced training.
Methods for Monitoring Heart Rate
- Heart Rate Monitors: Chest straps and wrist-worn devices provide accurate and continuous heart rate monitoring.
- Fitness Trackers: Many fitness trackers include heart rate monitoring features, offering convenience and data tracking.
- Manual Pulse Checks: You can manually check your pulse at your wrist (radial artery) or neck (carotid artery) by counting the number of beats in 15 seconds and multiplying by four.
Incorporating Heart Rate Zones into Your Workouts
- Determine Your Goals: Define your fitness goals, such as improving endurance, burning fat, or increasing speed.
- Calculate Your Heart Rate Zones: Use the formulas or consult with a healthcare professional to determine your MHR and heart rate zones.
- Design Your Workouts: Plan workouts that incorporate different heart rate zones to target specific fitness goals.
- Monitor Your Heart Rate: Use a heart rate monitor or manual pulse checks to stay within your target zones during workouts.
- Adjust as Needed: Adjust your workouts based on your heart rate response and how you feel.
Cardio Fitness Tests
Cardio fitness tests assess your cardiovascular health and aerobic capacity. Common tests include:
- VO2 Max Test: Measures the maximum amount of oxygen your body can use during exercise.
- Treadmill Test: Evaluates your heart’s response to increasing levels of exercise.
- Step Test: Measures your heart rate recovery after a set amount of stepping.
- Distance Run/Walk Test: Assesses how far you can run or walk in a set amount of time.
Tips for Improving Cardio Fitness
- Consistency is Key: Engage in regular cardio exercise at least three to five times per week.
- Gradual Progression: Gradually increase the intensity, duration, or frequency of your workouts.
- Variety: Incorporate different types of cardio exercises to challenge your body and prevent boredom.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body’s signals and rest when needed.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after workouts.
- Fuel Your Body: Eat a balanced diet to support your energy needs and recovery.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep per night to optimize recovery and performance.
Conclusion
Understanding heart rate zones and incorporating them into your cardio workouts is a powerful way to optimize your fitness and achieve your goals. By monitoring your heart rate and training within specific zones, you can tailor your workouts to improve endurance, burn fat, increase speed, and enhance overall cardiovascular health. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or certified trainer before starting any new exercise program. With consistency, dedication, and a strategic approach, you can unlock the numerous benefits of cardio fitness and live a healthier, more active life.







Leave a Reply