“Heart Disease in Patients with Autoimmune Disorders
Related Articles Heart Disease in Patients with Autoimmune Disorders
- Lifestyle Changes To Manage Chronic Conditions – Part 2
- Dietary Strategies For Coping With Chronic Diseases – Part 4
- Emerging Therapies For Managing Chronic Conditions – Part 7
- Palliative Care And Quality Of Life For Chronic Illness Patients – Part 9
- Dietary Strategies For Coping With Chronic Diseases – Part 6
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Heart Disease in Patients with Autoimmune Disorders. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Heart Disease in Patients with Autoimmune Disorders

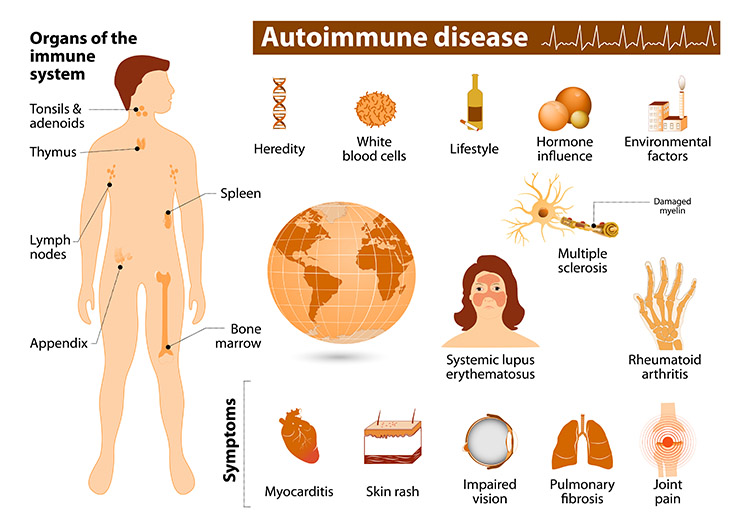
Autoimmune disorders are a group of conditions in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs. These disorders can affect various parts of the body, including the heart. Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, and patients with autoimmune disorders are at an increased risk of developing various cardiovascular complications. This article explores the connection between autoimmune disorders and heart disease, discussing the underlying mechanisms, specific autoimmune conditions associated with heart problems, diagnostic approaches, preventive measures, and management strategies.
Understanding the Connection Between Autoimmune Disorders and Heart Disease
The link between autoimmune disorders and heart disease is complex and multifaceted. Several factors contribute to the increased risk of cardiovascular complications in individuals with autoimmune conditions:
-
Chronic Inflammation: Autoimmune disorders are characterized by chronic inflammation, which plays a significant role in the development and progression of heart disease. Inflammation can damage the blood vessels, promote the formation of plaques, and disrupt the normal function of the heart muscle.
-
Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system’s dysregulation in autoimmune disorders can lead to the production of autoantibodies that target the heart tissue. These autoantibodies can directly damage the heart cells, causing inflammation and fibrosis.
-
Shared Risk Factors: Some risk factors for heart disease, such as smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, are more prevalent in individuals with autoimmune disorders. These shared risk factors further contribute to the increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
-
Medications: Certain medications used to treat autoimmune disorders, such as corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can have adverse effects on the cardiovascular system. These medications can increase blood pressure, promote fluid retention, and increase the risk of blood clots.
Specific Autoimmune Conditions Associated with Heart Problems
Several autoimmune disorders have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Some of the most notable conditions include:
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints but can also impact other organs, including the heart. Patients with RA have a higher risk of developing coronary artery disease, heart failure, and pericarditis.
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): SLE is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect various organs, including the heart. SLE patients are at an increased risk of developing pericarditis, myocarditis, valvular heart disease, and coronary artery disease.
-
Scleroderma: Scleroderma is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin and internal organs, including the heart. Scleroderma can lead to pulmonary hypertension, myocardial fibrosis, and pericarditis.
-
Sjögren’s Syndrome: Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the moisture-producing glands but can also involve other organs, including the heart. Sjögren’s syndrome has been associated with an increased risk of heart failure and arrhythmias.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the digestive tract but can also impact other organs, including the heart. IBD patients are at an increased risk of developing myocarditis, pericarditis, and venous thromboembolism.
Diagnostic Approaches for Heart Disease in Autoimmune Patients
Diagnosing heart disease in patients with autoimmune disorders can be challenging due to the overlapping symptoms and the potential for atypical presentations. A comprehensive evaluation is necessary to accurately diagnose and manage cardiovascular complications in these individuals. Diagnostic approaches may include:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough medical history and physical examination can provide valuable information about the patient’s symptoms, risk factors, and potential cardiovascular problems.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG is a noninvasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It can help detect arrhythmias, ischemia, and other abnormalities.
-
Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart that provides detailed information about the heart’s structure and function. It can help detect valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, and pericardial effusion.
-
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Cardiac MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that provides detailed images of the heart. It can help detect myocarditis, fibrosis, and other abnormalities.
-
Coronary Angiography: Coronary angiography is an invasive procedure that involves injecting dye into the coronary arteries to visualize them. It can help detect coronary artery disease.
-
Biomarkers: Blood tests can measure levels of certain biomarkers, such as troponin and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), which can indicate heart damage or heart failure.
Preventive Measures for Heart Disease in Autoimmune Patients
Preventing heart disease in patients with autoimmune disorders is crucial to improving their overall health and well-being. Preventive measures may include:
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
-
Managing Risk Factors: Controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes is essential for preventing cardiovascular complications.
-
Medications: Certain medications, such as statins and ACE inhibitors, can help lower cholesterol and blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.
-
Vaccinations: Vaccinations against influenza and pneumococcal pneumonia can help prevent infections that can exacerbate heart problems.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of cardiovascular health, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and ECGs, can help detect problems early and allow for timely intervention.
Management Strategies for Heart Disease in Autoimmune Patients
Managing heart disease in patients with autoimmune disorders requires a multidisciplinary approach involving cardiologists, rheumatologists, and other specialists. Management strategies may include:
-
Medications: Medications to treat heart disease, such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics, can help improve heart function and reduce symptoms.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Adhering to a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, is crucial for managing heart disease.
-
Cardiac Rehabilitation: Cardiac rehabilitation programs can help patients recover from heart events and improve their overall cardiovascular health.
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat heart disease, such as coronary artery bypass grafting or valve replacement.
-
Immunosuppressive Therapy: Immunosuppressive therapy may be necessary to control the underlying autoimmune disorder and reduce inflammation in the heart.
Conclusion
Heart disease is a significant concern for patients with autoimmune disorders. The chronic inflammation and immune system dysfunction associated with these conditions can increase the risk of various cardiovascular complications. Early diagnosis, preventive measures, and comprehensive management strategies are essential for improving the cardiovascular health of individuals with autoimmune disorders. By understanding the connection between autoimmune disorders and heart disease, healthcare professionals can provide better care and improve the quality of life for these patients.







Leave a Reply