“Economic Burden of Chronic Illnesses: A Global Perspective
Related Articles Economic Burden of Chronic Illnesses: A Global Perspective
- Lifestyle Changes To Manage Chronic Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Impact Of Chronic Illness On Mental Health
- Innovations In Treating Chronic Diseases
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to Economic Burden of Chronic Illnesses: A Global Perspective. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Economic Burden of Chronic Illnesses: A Global Perspective

Chronic illnesses represent a significant and growing challenge to healthcare systems and economies worldwide. Unlike acute conditions that are typically short-lived and curable, chronic diseases are long-lasting, often incurable, and require ongoing medical attention. These conditions, which include cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, chronic respiratory diseases, and mental disorders, not only affect individual health and well-being but also impose a substantial economic burden on societies.
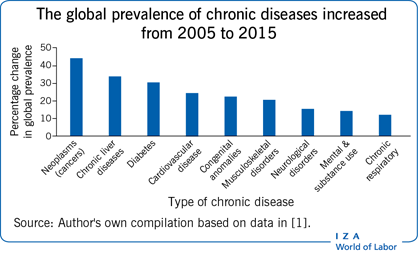
The Global Prevalence of Chronic Illnesses
The prevalence of chronic illnesses is increasing globally, driven by factors such as aging populations, lifestyle changes, and environmental factors. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), chronic diseases are the leading cause of death and disability worldwide, accounting for approximately 74% of all deaths globally. Low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) are disproportionately affected, with a higher burden of chronic diseases compared to high-income countries.
Direct Costs of Chronic Illnesses
The direct costs of chronic illnesses encompass the expenses associated with medical care, including hospitalizations, physician visits, diagnostic tests, medications, and rehabilitation services. These costs can be substantial, particularly for individuals with multiple chronic conditions or those requiring specialized care.
- Hospitalizations: Chronic illnesses often lead to frequent hospitalizations, which are among the most expensive components of healthcare. Patients with chronic conditions may require prolonged hospital stays, intensive care, and specialized procedures, contributing to significant hospital costs.
- Physician Visits: Regular visits to physicians and specialists are essential for managing chronic illnesses. These visits involve consultations, examinations, and monitoring of disease progression, resulting in considerable expenses for both patients and healthcare systems.
- Diagnostic Tests: Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial for effective management of chronic illnesses. Diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging scans, and biopsies, are essential for identifying and monitoring chronic conditions.
- Medications: Medications play a vital role in managing chronic illnesses, helping to control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. However, the cost of medications, particularly newer and more specialized drugs, can be a significant burden for patients and healthcare systems.
- Rehabilitation Services: Many chronic illnesses require rehabilitation services to help patients regain lost function, improve mobility, and enhance their overall well-being. Rehabilitation services may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, which can add to the direct costs of chronic illnesses.
Indirect Costs of Chronic Illnesses
In addition to direct medical costs, chronic illnesses also generate significant indirect costs, which include lost productivity, absenteeism, disability, and premature mortality. These costs are often overlooked but can have a substantial impact on individuals, families, and economies.
- Lost Productivity: Chronic illnesses can impair individuals’ ability to work, leading to reduced productivity and lost wages. Patients with chronic conditions may experience fatigue, pain, and other symptoms that interfere with their job performance.
- Absenteeism: Chronic illnesses can result in frequent absences from work, as patients may need to attend medical appointments, undergo treatments, or manage their symptoms. Absenteeism can lead to decreased productivity and increased costs for employers.
- Disability: In severe cases, chronic illnesses can lead to disability, preventing individuals from working altogether. Disability can result in a loss of income, reduced quality of life, and increased reliance on social support programs.
- Premature Mortality: Chronic illnesses can shorten life expectancy, leading to premature mortality. Premature deaths not only represent a loss of human potential but also result in significant economic costs, including lost productivity and reduced tax revenues.
The Economic Impact on Healthcare Systems
Chronic illnesses place a significant strain on healthcare systems, consuming a large proportion of healthcare resources. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases is driving up healthcare costs, making it more challenging for healthcare systems to provide affordable and accessible care to all.
- Increased Healthcare Spending: Chronic illnesses account for a substantial portion of healthcare spending in many countries. The costs associated with managing chronic conditions, such as hospitalizations, medications, and long-term care, contribute to rising healthcare expenditures.
- Resource Allocation Challenges: Healthcare systems face challenges in allocating resources to effectively manage chronic illnesses. Limited resources may need to be prioritized, potentially leading to reduced access to care for some patients.
- Strain on Healthcare Infrastructure: The increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses is putting a strain on healthcare infrastructure, including hospitals, clinics, and healthcare professionals. Healthcare systems may need to expand their capacity to accommodate the growing number of patients with chronic conditions.
The Economic Impact on Individuals and Families
Chronic illnesses can have a devastating economic impact on individuals and families. The costs associated with medical care, lost productivity, and other expenses can create financial hardship and strain household budgets.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Patients with chronic illnesses often face significant out-of-pocket expenses for medical care, including deductibles, co-payments, and uncovered services. These expenses can be a major burden, particularly for low-income individuals and families.
- Reduced Income: Chronic illnesses can lead to reduced income due to lost productivity, absenteeism, and disability. Reduced income can make it difficult for individuals and families to meet their basic needs and maintain their standard of living.
- Financial Strain: The economic burden of chronic illnesses can create financial strain and stress for individuals and families. Financial difficulties can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems.
Strategies to Mitigate the Economic Burden
Addressing the economic burden of chronic illnesses requires a multifaceted approach involving prevention, early detection, effective management, and supportive policies.
- Prevention: Preventing chronic illnesses is the most effective way to reduce their economic burden. Public health initiatives that promote healthy lifestyles, such as regular exercise, healthy diets, and smoking cessation, can help prevent the onset of chronic conditions.
- Early Detection: Early detection of chronic illnesses can improve treatment outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Screening programs and regular check-ups can help identify chronic conditions in their early stages, allowing for timely intervention.
- Effective Management: Effective management of chronic illnesses can help control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Comprehensive care plans, patient education, and self-management support can empower patients to actively participate in their care.
- Supportive Policies: Supportive policies, such as affordable healthcare, access to medications, and disability benefits, can help mitigate the economic burden of chronic illnesses. Governments and healthcare systems can implement policies that ensure access to affordable care and provide financial assistance to individuals and families affected by chronic conditions.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation can play a crucial role in reducing the economic burden of chronic illnesses. Telemedicine, remote monitoring, and mobile health applications can improve access to care, enhance patient engagement, and reduce healthcare costs.
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine allows patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits. Telemedicine can be particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas or those with mobility limitations.
- Remote Monitoring: Remote monitoring devices can track patients’ vital signs and other health data, allowing healthcare providers to monitor their condition remotely. Remote monitoring can help detect early signs of deterioration and prevent hospitalizations.
- Mobile Health Applications: Mobile health applications can provide patients with information, support, and tools to manage their chronic conditions. These applications can help patients track their medications, monitor their symptoms, and communicate with their healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Chronic illnesses pose a significant economic burden on individuals, families, healthcare systems, and economies worldwide. The direct and indirect costs of chronic diseases are substantial and are expected to continue to rise as the prevalence of these conditions increases. Addressing the economic burden of chronic illnesses requires a comprehensive approach involving prevention, early detection, effective management, and supportive policies. By investing in prevention, promoting early detection, improving management, and implementing supportive policies, we can reduce the economic burden of chronic illnesses and improve the health and well-being of individuals and communities.







Leave a Reply