“Community-Based Solutions to Reduce Heart Disease
Related Articles Community-Based Solutions to Reduce Heart Disease
- Leukemia Prevention Strategies: What You Need To Know
- Genetic Counseling In Families Affected By Leukemia
- Patient Empowerment In Chronic Disease Management
- Exercise And Physical Activity Guidelines For Chronic Illness Management – Part 5: Mental Health Conditions (Depression And Anxiety)
- Women’s Heart Health: Unique Risks And Challenges
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Community-Based Solutions to Reduce Heart Disease. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Community-Based Solutions to Reduce Heart Disease

Heart disease remains a leading cause of death worldwide, but its impact can be significantly reduced through community-based interventions. By addressing risk factors at the local level, communities can empower individuals to make healthier choices and create environments that support heart health. This article explores various community-based strategies that have proven effective in reducing heart disease risk and improving cardiovascular health outcomes.
Understanding Heart Disease
Heart disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and valve problems. The primary cause of heart disease is atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which restricts blood flow to the heart and other organs.
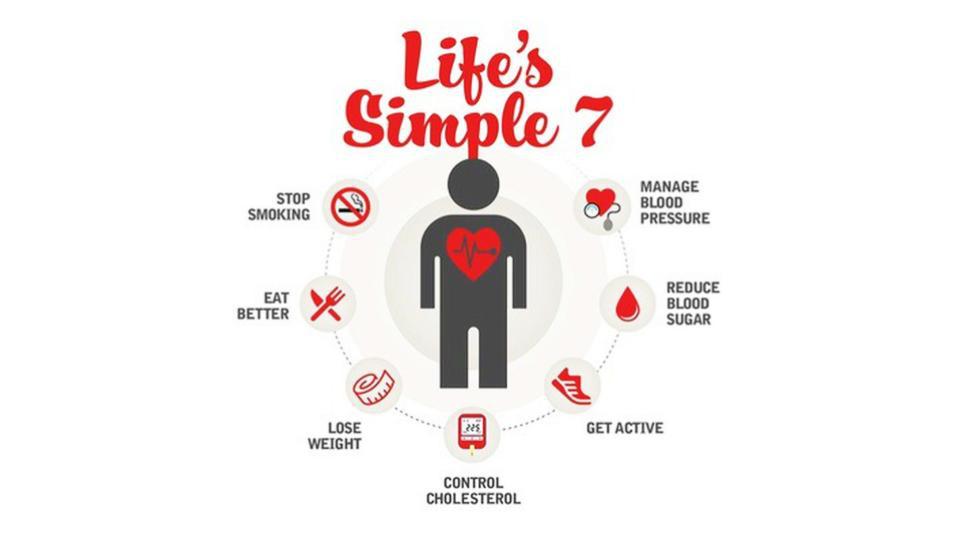
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Several risk factors contribute to the development of heart disease, including:
-
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.
-
High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol contribute to plaque formation in the arteries.
-
Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels, raises blood pressure, and increases the risk of blood clots, significantly increasing the risk of heart disease.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, is associated with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance, all of which increase the risk of heart disease.
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications.
-
Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of heart disease.
-
Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars increases the risk of heart disease, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein promotes heart health.
-
Family History: Individuals with a family history of heart disease are at higher risk of developing the condition themselves due to genetic predisposition.
Community-Based Solutions
Community-based interventions are essential for addressing the complex factors that contribute to heart disease. These strategies focus on creating healthier environments, promoting healthy behaviors, and improving access to healthcare services at the local level.
1. Health Education Programs
Health education programs play a crucial role in raising awareness about heart disease risk factors and promoting healthy behaviors. These programs can be delivered in various settings, including schools, workplaces, community centers, and healthcare facilities.
-
School-Based Programs: School-based programs can educate children and adolescents about the importance of healthy eating, physical activity, and avoiding tobacco use. These programs can incorporate interactive activities, games, and educational materials to engage students and promote behavior change.
-
Workplace Wellness Programs: Workplace wellness programs can encourage employees to adopt healthy habits through health screenings, educational workshops, and fitness challenges. These programs can also provide resources and support for employees to manage stress, quit smoking, and improve their overall health.
-
Community Health Campaigns: Community health campaigns can use mass media, social media, and community events to raise awareness about heart disease risk factors and promote healthy behaviors. These campaigns can target specific populations at high risk for heart disease, such as older adults, racial and ethnic minorities, and individuals with low incomes.
2. Promoting Healthy Eating
Promoting healthy eating is essential for reducing heart disease risk and improving overall health. Community-based interventions can focus on increasing access to healthy foods, providing nutrition education, and creating supportive environments for healthy eating.
-
Increasing Access to Healthy Foods: Communities can increase access to healthy foods by supporting farmers markets, community gardens, and mobile markets that bring fresh produce to underserved areas. They can also work with local grocery stores to stock healthier options and promote healthy eating through in-store promotions and educational displays.
-
Nutrition Education Programs: Nutrition education programs can teach individuals how to make healthy food choices, prepare nutritious meals, and read food labels. These programs can be delivered in various settings, including schools, community centers, and healthcare facilities.
-
Healthy Food Policies: Communities can implement policies that support healthy eating, such as restricting the sale of sugary drinks in schools, promoting healthy food options in vending machines, and providing incentives for restaurants to offer healthier menu items.
3. Encouraging Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, reducing blood pressure, lowering cholesterol, and improving overall cardiovascular health. Community-based interventions can focus on creating safe and accessible environments for physical activity, promoting active transportation, and offering exercise programs for people of all ages and abilities.
-
Creating Safe and Accessible Environments: Communities can create safe and accessible environments for physical activity by building parks, trails, and bike lanes. They can also improve pedestrian safety by installing sidewalks, crosswalks, and traffic calming measures.
-
Promoting Active Transportation: Communities can promote active transportation by encouraging people to walk, bike, or take public transportation instead of driving. They can do this by providing incentives for using active transportation, such as bike-sharing programs and subsidized transit passes.
-
Exercise Programs: Communities can offer exercise programs for people of all ages and abilities, such as walking groups, fitness classes, and sports leagues. These programs can be offered in various settings, including community centers, parks, and healthcare facilities.
4. Tobacco Control Programs
Tobacco use is a leading cause of heart disease, cancer, and other chronic diseases. Community-based tobacco control programs can reduce tobacco use by preventing initiation, promoting cessation, and protecting people from secondhand smoke.
-
Prevention Programs: Prevention programs can educate young people about the dangers of tobacco use and discourage them from starting to smoke. These programs can be delivered in schools, community centers, and healthcare facilities.
-
Cessation Programs: Cessation programs can help smokers quit by providing counseling, medication, and support. These programs can be offered in various settings, including healthcare facilities, workplaces, and community centers.
-
Smoke-Free Policies: Smoke-free policies can protect people from secondhand smoke by prohibiting smoking in public places, workplaces, and multi-unit housing. These policies can reduce exposure to secondhand smoke, which is a known cause of heart disease and other health problems.
5. Hypertension and Cholesterol Management
Hypertension and high cholesterol are major risk factors for heart disease. Community-based interventions can improve hypertension and cholesterol management by increasing awareness, promoting screening, and providing access to treatment.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Awareness campaigns can educate people about the importance of getting their blood pressure and cholesterol checked regularly. These campaigns can use mass media, social media, and community events to reach a wide audience.
-
Screening Programs: Screening programs can provide free or low-cost blood pressure and cholesterol screenings at community events, healthcare facilities, and workplaces. These programs can help identify people who are at risk for heart disease and refer them to appropriate care.
-
Access to Treatment: Communities can improve access to treatment for hypertension and high cholesterol by expanding access to affordable healthcare, providing medication assistance programs, and promoting adherence to treatment plans.
6. Community Health Workers
Community health workers (CHWs) play a vital role in connecting individuals with healthcare services and promoting healthy behaviors. CHWs are trusted members of the community who can provide culturally appropriate health education, outreach, and support.
-
Health Education: CHWs can provide health education on various topics, including heart disease prevention, healthy eating, physical activity, and tobacco cessation. They can also provide education on managing chronic conditions, such as hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
-
Outreach: CHWs can conduct outreach to identify individuals who are at risk for heart disease and connect them with healthcare services. They can also provide support to individuals who are struggling to manage their health.
-
Support: CHWs can provide emotional support, encouragement, and practical assistance to individuals who are trying to adopt healthy behaviors or manage chronic conditions. They can also help individuals navigate the healthcare system and access resources and services.
7. Policy and Environmental Changes
Policy and environmental changes can create supportive environments for heart health by making healthy choices easier and more accessible. These changes can include policies that promote healthy eating, physical activity, and tobacco control.
-
Healthy Eating Policies: Policies that promote healthy eating can include taxes on sugary drinks, subsidies for healthy foods, and restrictions on marketing unhealthy foods to children.
-
Physical Activity Policies: Policies that promote physical activity can include funding for parks, trails, and bike lanes, and incentives for using active transportation.
-
Tobacco Control Policies: Policies that control tobacco can include taxes on tobacco products, smoke-free policies, and restrictions on tobacco advertising.
Conclusion
Heart disease is a preventable condition, and community-based interventions can play a crucial role in reducing its impact. By addressing risk factors at the local level, communities can empower individuals to make healthier choices and create environments that support heart health. Through health education programs, promotion of healthy eating and physical activity, tobacco control programs, hypertension and cholesterol management, community health workers, and policy and environmental changes, communities can significantly reduce heart disease risk and improve cardiovascular health outcomes. It is essential for communities to adopt a comprehensive approach that addresses multiple risk factors and engages diverse stakeholders to achieve lasting improvements in heart health.







Leave a Reply