“Comorbidities Associated with Common Chronic Diseases
Related Articles Comorbidities Associated with Common Chronic Diseases
- Integrative Medicine In Chronic Disease Care
- The Impact Of Chronic Illness On Mental Health
- Emerging Therapies For Managing Chronic Conditions: A Glimpse Into The Future Of Healthcare
- Innovations In Treating Chronic Diseases
- Innovations In Treating Chronic Diseases
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Comorbidities Associated with Common Chronic Diseases. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Comorbidities Associated with Common Chronic Diseases

Chronic diseases are long-lasting health conditions that cannot be cured but can be controlled. They are the leading cause of death and disability in the United States, and they also contribute significantly to healthcare costs. The most common chronic diseases include heart disease, stroke, cancer, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and arthritis.
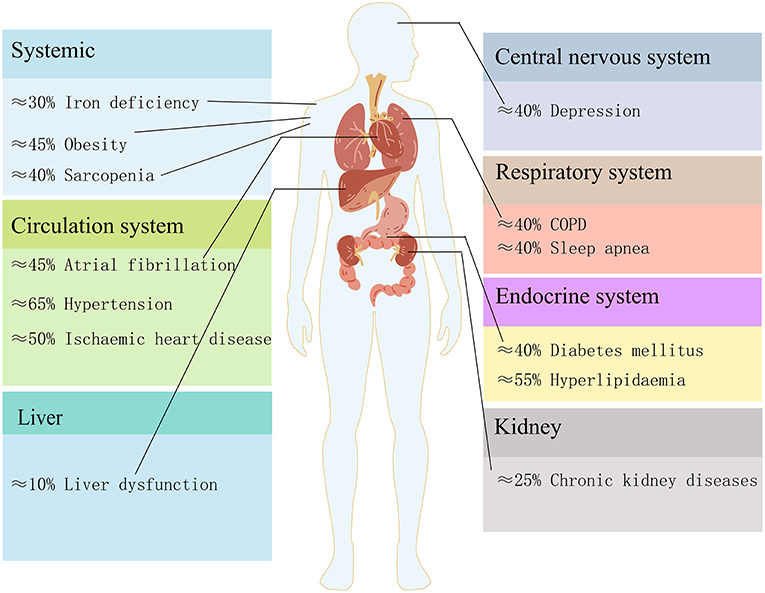
One of the biggest challenges in managing chronic diseases is that they often occur together. This is known as comorbidity, which is the presence of two or more chronic diseases in the same person. Comorbidities can make it more difficult to manage chronic diseases, as they can interact with each other and make symptoms worse. They can also increase the risk of complications and death.
Risk Factors for Comorbidities
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing comorbidities. These include:
- Age: The risk of developing chronic diseases increases with age. As people age, they are more likely to develop multiple chronic conditions.
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to developing certain chronic diseases. This can increase their risk of developing comorbidities.
- Lifestyle: Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise, can increase the risk of developing chronic diseases and comorbidities.
- Socioeconomic status: People with lower socioeconomic status are more likely to develop chronic diseases and comorbidities. This may be due to factors such as limited access to healthcare, poor nutrition, and exposure to environmental hazards.
Common Comorbidities
Some of the most common comorbidities associated with chronic diseases include:
- Heart disease and stroke: Heart disease and stroke are two of the leading causes of death in the United States. They often occur together, as they share many of the same risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking.
- Heart disease and diabetes: Heart disease is a major complication of diabetes. People with diabetes are more likely to develop heart disease than people without diabetes. This is because diabetes can damage the blood vessels and nerves, which can lead to heart disease.
- Cancer and diabetes: People with diabetes are also at increased risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer, breast cancer, and endometrial cancer. This may be due to the fact that diabetes can increase the levels of insulin and other growth factors in the body, which can promote cancer growth.
- Obesity and diabetes: Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. People who are obese are more likely to develop insulin resistance, which can lead to diabetes.
- Obesity and heart disease: Obesity is also a major risk factor for heart disease. People who are obese are more likely to have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and other risk factors for heart disease.
- Arthritis and heart disease: People with arthritis are at increased risk of developing heart disease. This may be due to the fact that arthritis can cause inflammation, which can damage the blood vessels and lead to heart disease.
- Mental health conditions and chronic diseases: Mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, are often comorbid with chronic diseases. People with chronic diseases are more likely to experience mental health problems, and people with mental health problems are more likely to develop chronic diseases.
Impact of Comorbidities
Comorbidities can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of people with chronic diseases. They can:
- Make it more difficult to manage chronic diseases: Comorbidities can interact with each other and make symptoms worse. For example, someone with both heart disease and diabetes may have more difficulty controlling their blood sugar levels and blood pressure.
- Increase the risk of complications: Comorbidities can increase the risk of complications from chronic diseases. For example, someone with both heart disease and diabetes is at increased risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
- Increase the risk of death: Comorbidities can increase the risk of death from chronic diseases. For example, someone with both heart disease and diabetes is at increased risk of dying from heart disease.
- Reduce quality of life: Comorbidities can reduce quality of life by causing pain, fatigue, and other symptoms. They can also make it difficult to participate in activities that people enjoy.
- Increase healthcare costs: Comorbidities can increase healthcare costs by requiring more frequent doctor visits, hospitalizations, and medications.
Managing Comorbidities
Managing comorbidities can be challenging, but it is important to do so to improve health outcomes and quality of life. Some strategies for managing comorbidities include:
- Comprehensive assessment: A thorough assessment is essential to identify all existing chronic conditions and potential comorbidities.
- Individualized treatment plan: A treatment plan should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and address all of their chronic conditions.
- Lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, can help to manage many chronic diseases and comorbidities.
- Medications: Medications can be used to manage chronic diseases and comorbidities. It is important to talk to your doctor about the potential side effects of medications and how they may interact with each other.
- Self-management education: Self-management education can help people with chronic diseases and comorbidities learn how to manage their conditions and improve their health.
- Coordination of care: Coordination of care between different healthcare providers is essential to ensure that people with chronic diseases and comorbidities receive the best possible care.
- Regular monitoring: Regular monitoring of chronic conditions and comorbidities is essential to detect problems early and prevent complications.
- Mental health support: Mental health support can help people with chronic diseases and comorbidities cope with the emotional challenges of their conditions.
- Social support: Social support from family, friends, and support groups can help people with chronic diseases and comorbidities feel less isolated and more supported.
Prevention of Comorbidities
While some comorbidities are unavoidable, many can be prevented by adopting healthy lifestyle habits. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet: A healthy diet can help to prevent obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic diseases.
- Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help to prevent obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic diseases.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help to prevent obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic diseases.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for many chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, cancer, and lung disease.
- Managing stress: Stress can contribute to many chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
- Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep can help to improve overall health and well-being and may help to prevent chronic diseases.
- Getting regular checkups: Regular checkups can help to detect chronic diseases early, when they are more treatable.
Conclusion
Comorbidities are a common and complex challenge in healthcare. They can make it more difficult to manage chronic diseases, increase the risk of complications and death, and reduce quality of life. However, by understanding the risk factors for comorbidities, implementing effective management strategies, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, it is possible to improve the health and well-being of people with chronic diseases and comorbidities. Early detection, comprehensive management, and a focus on preventive measures are crucial in addressing the challenges posed by comorbidities.







Leave a Reply