“Bone Health and Healthcare Equity: Addressing Disparities for Stronger Communities
Related Articles Bone Health and Healthcare Equity: Addressing Disparities for Stronger Communities
- Bone Health And Climate Change: An Emerging Threat
- Bone Health Education: Promoting Awareness And Prevention
- Bone Health During Pregnancy And Lactation
- Bone Health And Respiratory Diseases: An Intertwined Relationship
- Bone Health And Mental Health: Exploring Connections
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Bone Health and Healthcare Equity: Addressing Disparities for Stronger Communities. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Bone Health and Healthcare Equity: Addressing Disparities for Stronger Communities
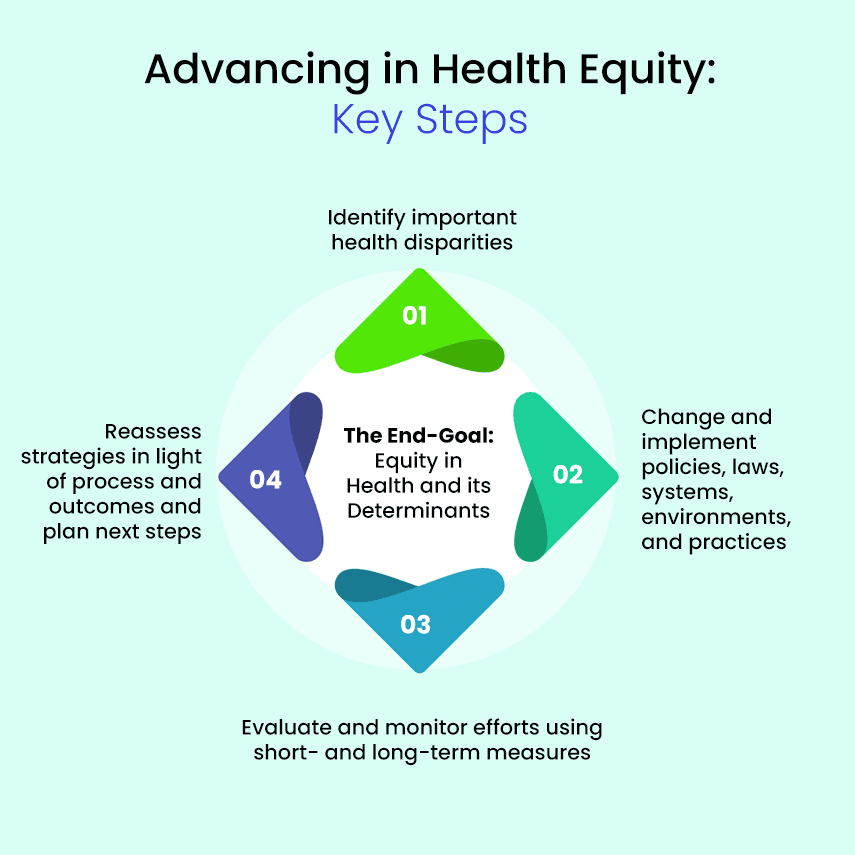
Bone health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, influencing mobility, independence, and quality of life. However, bone health is not uniformly distributed across all populations. Significant disparities exist, with certain racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups experiencing a disproportionate burden of bone-related diseases, such as osteoporosis and fractures. Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach that considers the complex interplay of biological, behavioral, and socioeconomic factors that contribute to healthcare inequities.
The Importance of Bone Health
Bones provide structural support, protect vital organs, and store essential minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus. Maintaining bone health throughout life is crucial for preventing fractures, reducing pain, and preserving physical function. Peak bone mass is typically achieved in early adulthood, after which bone density gradually declines with age. Several factors can influence bone health, including genetics, diet, physical activity, hormonal balance, and certain medical conditions.
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by low bone density and increased risk of fractures, is a major public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. Osteoporotic fractures can lead to significant pain, disability, and reduced quality of life. Hip fractures, in particular, are associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality.
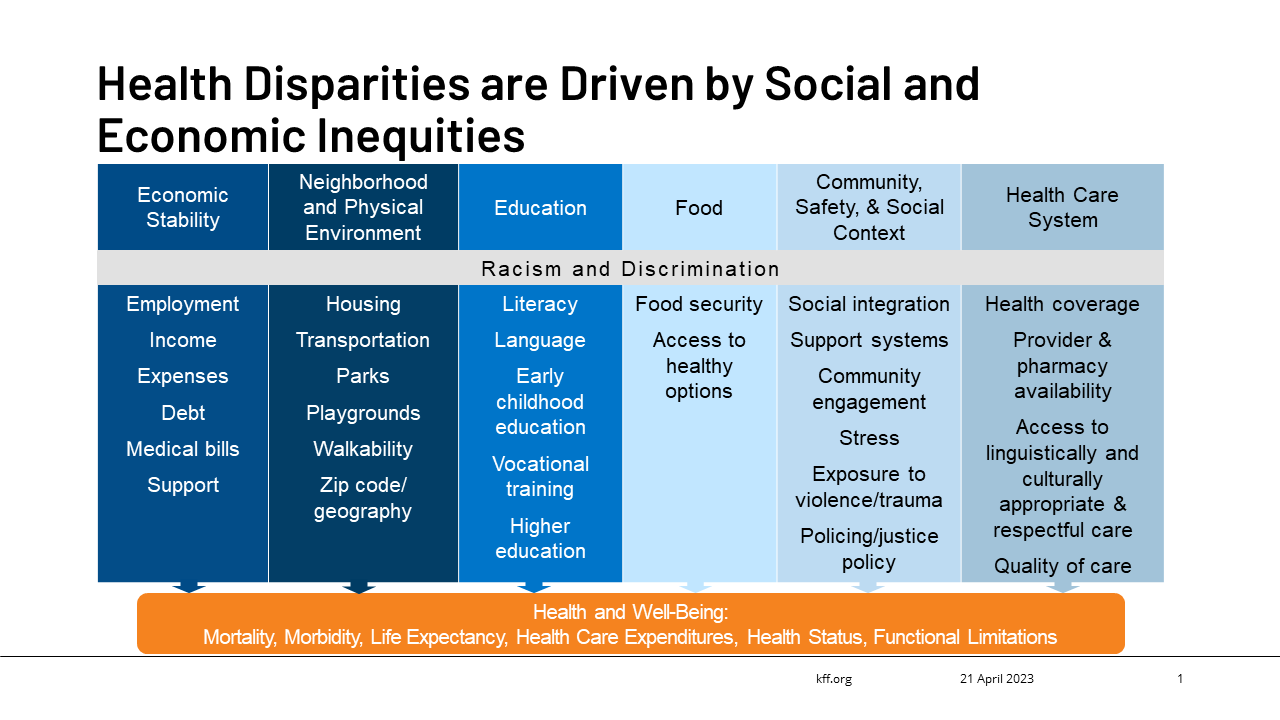
Disparities in Bone Health
Despite the importance of bone health, significant disparities exist in the prevalence and outcomes of bone-related diseases. These disparities are often linked to systemic inequities in healthcare access, socioeconomic status, and environmental factors.
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Studies have consistently shown that certain racial and ethnic groups are at higher risk of osteoporosis and fractures compared to others. For example, African Americans tend to have higher bone density than Caucasians, but they also experience higher rates of hip fractures and poorer outcomes after fracture. This may be due to differences in bone geometry, vitamin D levels, and access to healthcare. Hispanic/Latino individuals also face disparities in bone health, with lower rates of screening and treatment for osteoporosis.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Socioeconomic status plays a significant role in bone health. Individuals from low-income backgrounds often have limited access to nutritious food, healthcare services, and safe environments for physical activity. These factors can negatively impact bone development and increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Geographic Disparities: Geographic location can also influence bone health. People living in rural areas may have limited access to healthcare providers and diagnostic facilities, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis. Additionally, certain geographic regions may have lower sunlight exposure, resulting in vitamin D deficiency, which is essential for bone health.
- Gender Disparities: Women are at higher risk of osteoporosis than men due to hormonal changes associated with menopause. However, men are also affected by osteoporosis, and they tend to have poorer outcomes after fractures.
Factors Contributing to Bone Health Disparities
Several factors contribute to the observed disparities in bone health. These factors can be broadly categorized as biological, behavioral, and socioeconomic.
- Biological Factors: Genetic factors play a role in bone density and fracture risk. Certain genes have been associated with increased susceptibility to osteoporosis. Additionally, hormonal factors, such as estrogen levels, can significantly impact bone health, particularly in women.
- Behavioral Factors: Lifestyle choices, such as diet, physical activity, and smoking, can influence bone health. A diet lacking in calcium and vitamin D can impair bone development and increase the risk of osteoporosis. Similarly, lack of weight-bearing exercise can weaken bones. Smoking has been shown to negatively impact bone density and increase fracture risk.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic factors, such as income, education, and access to healthcare, play a critical role in bone health. Individuals from low-income backgrounds may have limited access to nutritious food, healthcare services, and safe environments for physical activity. Lack of health insurance can also prevent people from receiving timely screening and treatment for osteoporosis.
Addressing Bone Health Disparities
Addressing bone health disparities requires a comprehensive approach that considers the complex interplay of biological, behavioral, and socioeconomic factors. Strategies to reduce disparities should focus on improving access to healthcare, promoting healthy lifestyles, and addressing systemic inequities.
- Improving Access to Healthcare: Expanding access to healthcare services is essential for reducing bone health disparities. This includes increasing the availability of primary care providers, specialists, and diagnostic facilities in underserved communities. Telehealth can also be used to improve access to care for people living in rural areas.
- Promoting Healthy Lifestyles: Promoting healthy lifestyles is crucial for preventing osteoporosis and fractures. This includes encouraging people to consume a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engage in regular weight-bearing exercise, and avoid smoking. Public health campaigns can be used to raise awareness about the importance of bone health and promote healthy behaviors.
- Addressing Systemic Inequities: Addressing systemic inequities is essential for creating a more equitable healthcare system. This includes addressing issues such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to education and employment opportunities. Policies that promote economic security and social justice can help improve bone health outcomes for all populations.
- Culturally Competent Care: Healthcare providers should be trained to provide culturally competent care that is sensitive to the needs of diverse populations. This includes understanding the cultural beliefs and practices that may influence bone health behaviors. Culturally tailored interventions can be more effective in promoting healthy lifestyles and improving bone health outcomes.
- Community-Based Interventions: Community-based interventions can be effective in reaching underserved populations and promoting bone health. These interventions can be tailored to the specific needs of the community and can involve partnerships with local organizations, such as churches, schools, and community centers.
- Research and Data Collection: More research is needed to understand the underlying causes of bone health disparities and to develop effective interventions. Data collection efforts should focus on gathering information about race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and other factors that may contribute to disparities.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a critical role in promoting bone health and addressing disparities. They can educate patients about the importance of bone health, screen for osteoporosis, and provide appropriate treatment. Healthcare professionals should also be aware of the disparities in bone health and should be trained to provide culturally competent care.
- Education and Counseling: Healthcare professionals should educate patients about the importance of bone health and the factors that can influence bone density. They should also provide counseling on how to maintain bone health through diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications.
- Screening and Diagnosis: Healthcare professionals should screen patients for osteoporosis based on risk factors and guidelines. Bone density testing, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), can be used to diagnose osteoporosis.
- Treatment and Management: Healthcare professionals should provide appropriate treatment for osteoporosis, including medications to increase bone density and reduce fracture risk. They should also provide guidance on fall prevention and other strategies to reduce the risk of fractures.
- Advocacy: Healthcare professionals can advocate for policies that promote bone health and address healthcare disparities. This includes supporting policies that expand access to healthcare, promote healthy lifestyles, and address systemic inequities.
Conclusion
Bone health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and disparities in bone health exist across racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups. Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach that considers the complex interplay of biological, behavioral, and socioeconomic factors. By improving access to healthcare, promoting healthy lifestyles, addressing systemic inequities, and providing culturally competent care, we can reduce bone health disparities and create stronger, healthier communities. Healthcare professionals play a critical role in promoting bone health and advocating for policies that address healthcare disparities. By working together, we can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to maintain strong bones and live a healthy, active life.







Leave a Reply