“Bone Health and Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Complex Interplay
Related Articles Bone Health and Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Complex Interplay
- Bone Grafting: Procedures And Applications
- Bone Metabolism Disorders: Overview And Management
- Bone Health Education: Promoting Awareness And Prevention
- The Role Of Hormones In Bone Growth And Development
- Bone Infections: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to Bone Health and Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Complex Interplay. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Bone Health and Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Complex Interplay
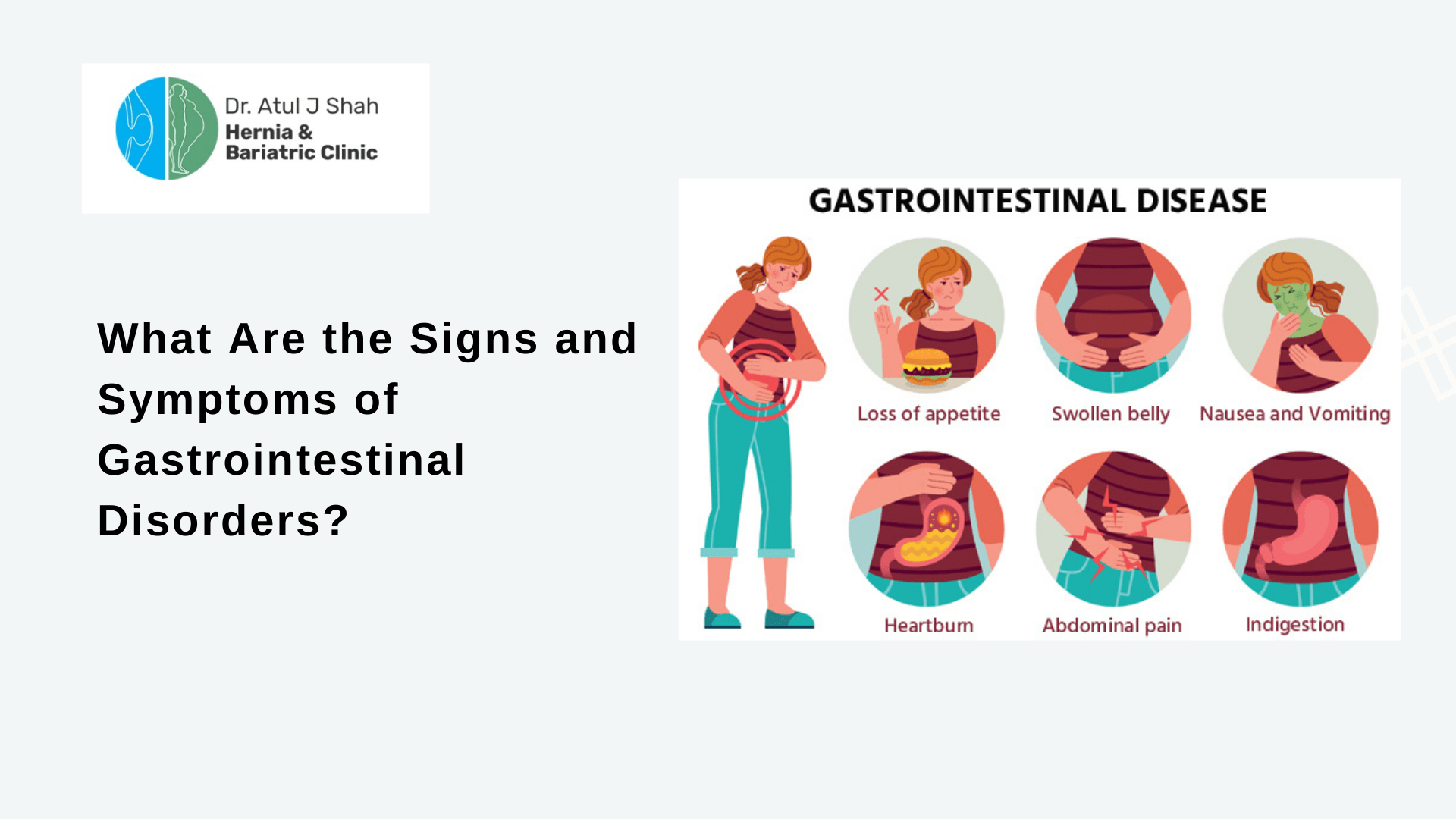
Bone health and gastrointestinal (GI) health may seem like separate aspects of overall well-being, but they are intricately connected. The GI system plays a crucial role in absorbing nutrients essential for bone health, such as calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin K. When the GI system is compromised by disorders, it can lead to malabsorption of these vital nutrients, subsequently impacting bone health and increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
The Importance of Bone Health
Bones are dynamic living tissues that constantly undergo remodeling, a process involving the breakdown of old bone and the formation of new bone. This process is essential for maintaining bone strength and density throughout life. Bone health is particularly important during childhood and adolescence when bones are growing rapidly. Adequate calcium intake and vitamin D levels during these years are crucial for building strong bones that can withstand the demands of daily life.
As we age, bone remodeling slows down, and bone loss can occur more rapidly than bone formation. This can lead to a decrease in bone density, making bones more fragile and susceptible to fractures. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by low bone density and increased fracture risk, is a major public health concern, especially among older adults.
The Role of the Gastrointestinal System in Bone Health
The GI system is responsible for digesting food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. It plays a vital role in bone health by absorbing essential nutrients, including:
- Calcium: Calcium is the primary mineral component of bone, providing strength and rigidity. The GI system absorbs calcium from food and supplements, and this calcium is then deposited in bone tissue.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption. It helps the GI system absorb calcium from food and regulates calcium levels in the blood. Vitamin D is produced in the skin when exposed to sunlight and can also be obtained from certain foods and supplements.
- Vitamin K: Vitamin K is important for bone formation and mineralization. It helps activate proteins involved in bone metabolism and promotes the deposition of calcium in bone tissue. Vitamin K is found in green leafy vegetables and is also produced by bacteria in the gut.
- Magnesium: Magnesium plays a role in bone structure and strength. It helps regulate calcium and vitamin D metabolism and is involved in bone remodeling.
- Protein: Protein is essential for bone matrix formation. It provides the building blocks for collagen, the main structural protein in bone.
Gastrointestinal Disorders That Can Impact Bone Health
Several GI disorders can interfere with nutrient absorption and negatively impact bone health. These include:
- Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. In people with celiac disease, gluten triggers an immune response that damages the small intestine, leading to malabsorption of nutrients, including calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin K.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation of the GI tract. This inflammation can interfere with nutrient absorption and lead to malabsorption of calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients.
- Lactose Intolerance: Lactose intolerance is the inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. People with lactose intolerance may avoid dairy products, which are a good source of calcium, potentially leading to calcium deficiency.
- Gastric Bypass Surgery: Gastric bypass surgery is a weight-loss procedure that involves creating a small pouch in the stomach and bypassing a portion of the small intestine. This can lead to malabsorption of nutrients, including calcium and vitamin D.
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Chronic pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas produces enzymes that are essential for digestion. When the pancreas is damaged, it can lead to malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamin D and vitamin K.
- Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS): SBS occurs when a significant portion of the small intestine is removed or damaged, leading to impaired nutrient absorption. This can result in deficiencies in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients.
Consequences of Malabsorption on Bone Health
Malabsorption of nutrients due to GI disorders can have several negative consequences on bone health, including:
- Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by low bone density and increased fracture risk. Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Osteomalacia: Osteomalacia is a condition characterized by soft bones due to vitamin D deficiency. Malabsorption of vitamin D can lead to osteomalacia, which can cause bone pain, muscle weakness, and an increased risk of fractures.
- Increased Fracture Risk: Malabsorption of nutrients can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist.
- Delayed Growth and Development in Children: In children, malabsorption of nutrients can lead to delayed growth and development, including impaired bone growth.
Diagnosis and Management
If you have a GI disorder, it is important to be aware of the potential impact on your bone health. Talk to your doctor about your risk factors for bone loss and whether you need to be screened for osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency.
Diagnosis of bone health issues related to GI disorders may involve:
- Bone Density Test (DEXA Scan): A DEXA scan measures bone density and can help diagnose osteoporosis.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrient levels.
- Stool Tests: Stool tests can help diagnose malabsorption.
Management of bone health issues related to GI disorders typically involves:
- Treating the Underlying GI Disorder: Treating the underlying GI disorder is essential for improving nutrient absorption and bone health. This may involve medications, dietary changes, or surgery.
- Supplementation: Supplementation with calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients may be necessary to correct deficiencies and improve bone health.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as regular weight-bearing exercise and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can also help improve bone health.
- Medications for Osteoporosis: If you have osteoporosis, your doctor may prescribe medications to help increase bone density and reduce fracture risk.
Preventive Measures
While individuals with GI disorders are at a higher risk, everyone can take steps to promote bone health and minimize the risk of developing osteoporosis:
- Adequate Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: Consume a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D. Dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods are good sources of calcium. Vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight exposure, fortified foods, and supplements.
- Regular Weight-Bearing Exercise: Engage in weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, and dancing to help strengthen bones.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can negatively impact bone health.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help identify and address potential risk factors for bone loss.
Conclusion
The connection between bone health and GI disorders is undeniable. GI disorders can impair nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies that negatively impact bone health. Individuals with GI disorders should be aware of the potential impact on their bones and take steps to maintain bone health through proper treatment, supplementation, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring. By addressing both the GI disorder and bone health concerns, individuals can improve their overall well-being and reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. A proactive approach involving healthcare professionals is essential for managing this complex interplay and ensuring optimal bone health.








Leave a Reply